A Comprehensive Guide to Infant Gas: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and effective remedies for infant gas. It offers valuable insights into managing baby bloating, including feeding techniques, natural remedies, and when to seek medical advice. Parents can use these practical tips to soothe their infants, ensuring better comfort and health during critical developmental stages. Understanding infant digestion is essential for fostering a happy, fuss-free baby and building a strong foundation for healthy growth.
A Comprehensive Guide to Infant Gas: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
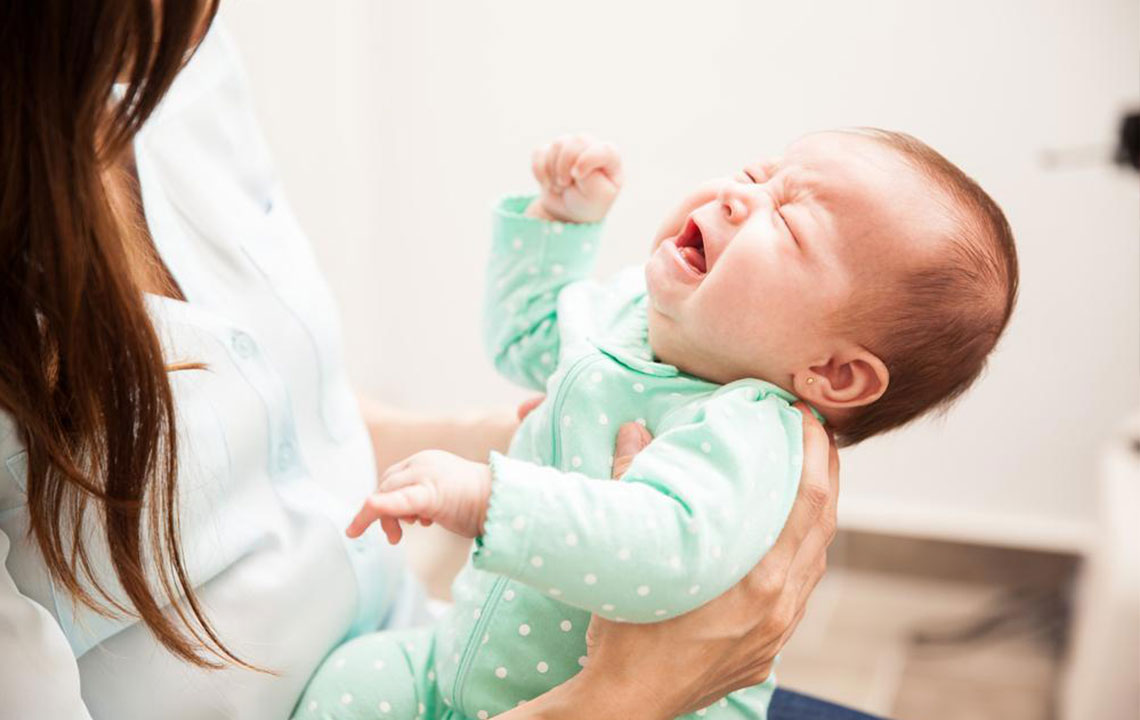
Infants often face digestive challenges, with stomach bloating and gas being some of the most common issues that lead to discomfort, fussiness, and sleep disturbances. Baby gas occurs when gas-forming substances accumulate in the immature digestive system, making infants irritable and uncomfortable. This condition, if not managed properly, can interfere with feeding routines and overall well-being. Early recognition and effective management of infant gas are crucial for ensuring their comfort, healthy growth, and development. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and remedies for baby gas can help parents provide relief and promote a happier, healthier baby.
Various over-the-counter remedies are available for alleviating infant gas. These include specialized drops and gels that contain simethicone or other safe ingredients approved for infants. Feeding habits play a significant role; offering small, frequent meals rather than large ones can help reduce gas build-up. Maintaining consistent feeding schedules prevents overstretching a baby’s delicate digestive system. Selecting easily digestible, nutrient-rich foods supports optimal digestion, whereas high-protein foods might lead to indigestion and discomfort. In severe cases, it’s advisable to seek medical advice; pediatricians may recommend specific treatments or medications to ease gas issues. Gentle abdominal massages using lukewarm oil, effective burping techniques, and proper feeding positions—such as keeping the baby's head elevated during feeds—are simple yet effective practices to reduce trapped air and discomfort. Gradually transitioning the baby from soft to more solid foods can also minimize digestive disturbances.
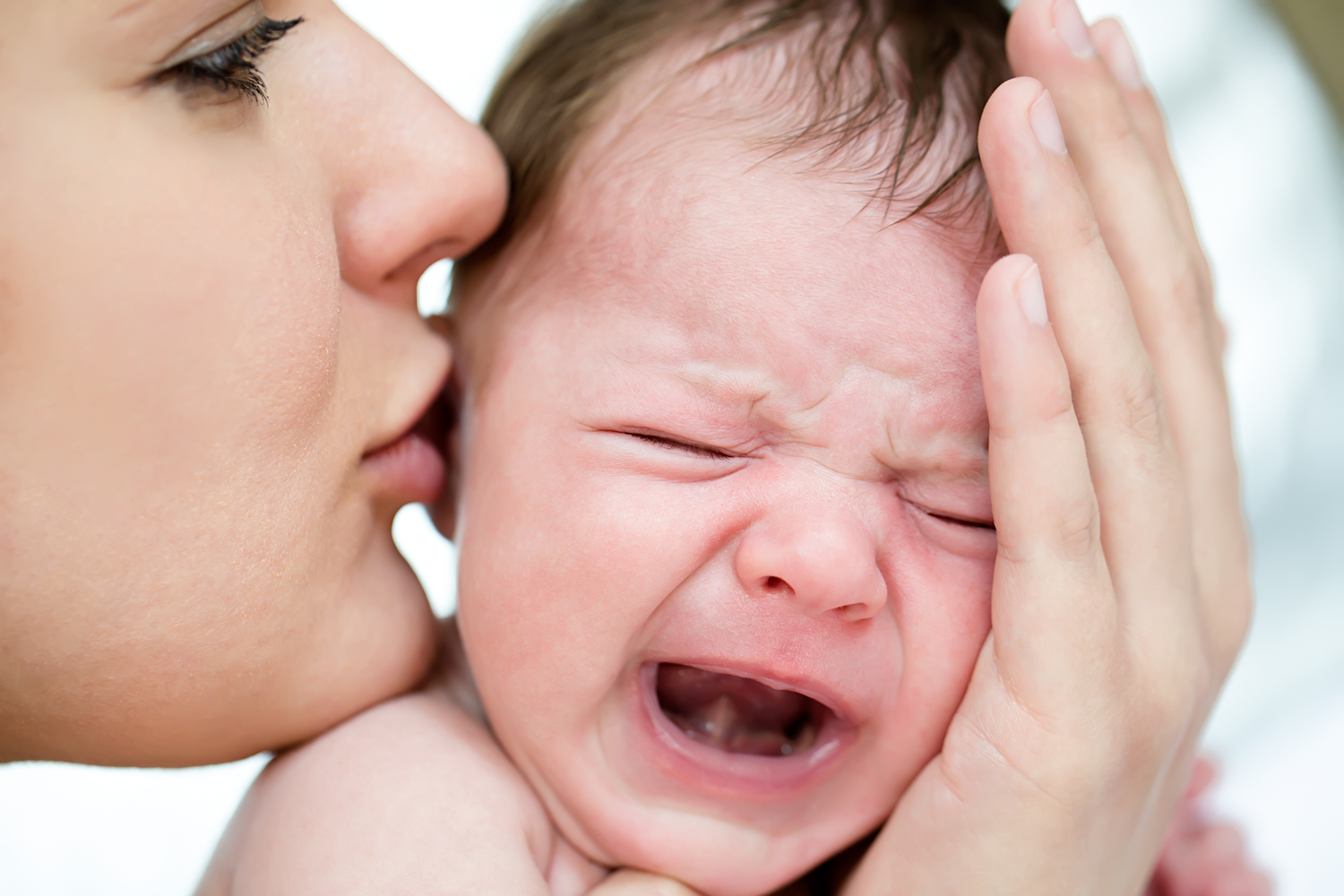
Monitoring maternal diet is equally important, especially for breastfeeding mothers, as certain foods can influence the infant’s digestion. Foods like beans, leafy greens, dried fruits, and raw vegetables are known to cause increased gas in breastfed babies. Parents should adopt gentle feeding techniques—feeding slowly, stopping frequently to burp, and avoiding rushing the process—to limit air intake. Massaging the baby’s abdomen in a clockwise motion helps release trapped gas and promotes digestive comfort. Ensuring the baby remains in a comfortable feeding position, such as keeping the head elevated, reduces the chance of swallowing excess air. When introducing new foods—particularly cow's milk or potential allergens—adding them gradually allows the infant’s digestive system to adapt, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal upset. These simple, informed precautions contribute to providing a safe, comfortable, and nurturing feeding environment, supporting the baby’s overall health and development.




