Cutting-Edge Strategies for Effective Asthma Management and Treatment
This comprehensive article explores innovative and traditional approaches to managing asthma effectively. It covers rescue medications, long-term control strategies, emerging treatments like bronchial thermoplasty, and the latest advancements in inhaler technology. Learn how cutting-edge therapies and careful monitoring can improve quality of life for asthma patients, reducing attacks and side effects while providing personalized care options. Stay informed about the future of asthma management and ensure optimal health outcomes with these expert insights.

Cutting-Edge Strategies for Effective Asthma Management and Treatment
Asthma is a widespread chronic respiratory disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. Despite being a long-term condition, asthma can often be effectively managed with a comprehensive treatment strategy that includes immediate relief measures, long-term control, and innovative therapeutic approaches. Over the years, advancements in medical technology and new treatment options have significantly improved outcomes for asthma patients, reducing hospital visits and enhancing quality of life.
In asthma management, rapid symptom relief is critical during acute exacerbations. Quick-relief medications, also known as rescue drugs, are essential for controlling sudden attacks. These medications commonly include short-acting beta-agonists, which act promptly by relaxing airway muscles, thereby opening the airways and making breathing easier. Usage of these rescue inhalers should be carefully monitored to avoid overuse, which can lead to decreased effectiveness or side effects. While traditional medications like inhalers have been foundational, recent innovations have introduced smarter devices that improve delivery accuracy and adherence.
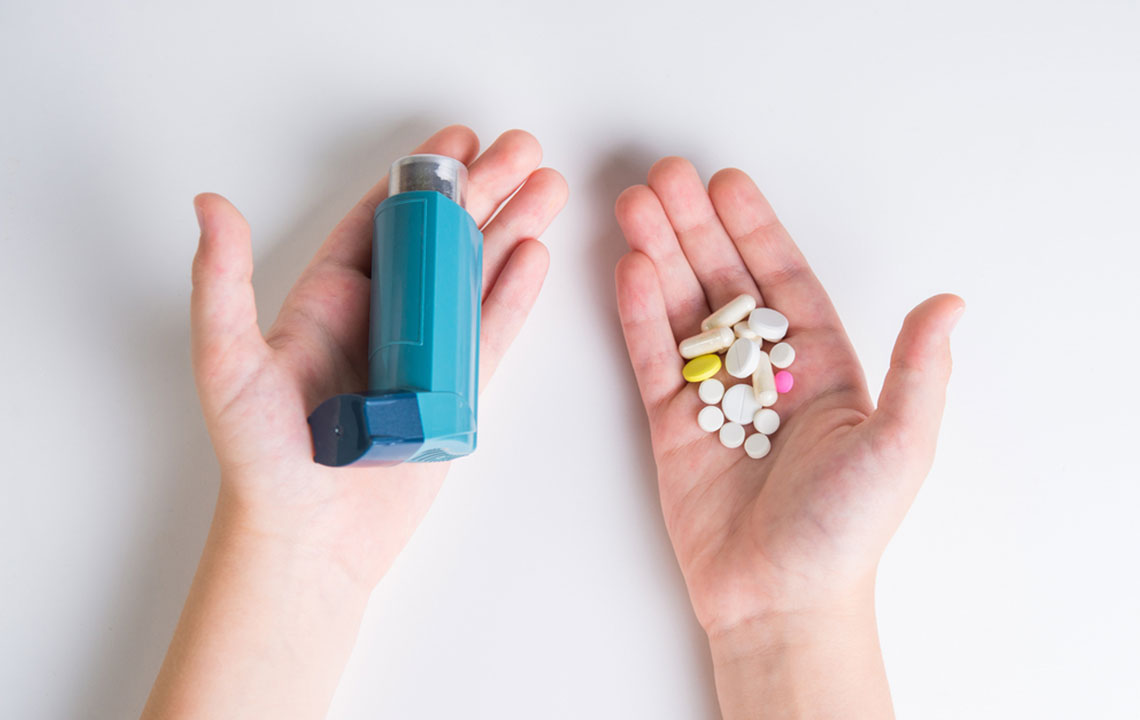
Standard treatments for persistent asthma often involve inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists, and leukotriene modifiers. Interestingly, many of these medications were initially developed for conditions such as emphysema but have proven effective in managing severe asthma symptoms, including persistent wheezing, chest tightness, and breathlessness. Both oral and intravenous (IV) options are available for rapid symptom relief, especially in emergency settings. However, frequent reliance on these systemic medications can sometimes lead to side effects like increased heart rate, jitteriness, and other systemic issues. To minimize these risks, healthcare providers emphasize the importance of tailored treatment plans that balance immediate symptom control with long-term safety.
Long-term asthma control is equally vital to prevent frequent attacks and reduce dependence on rescue drugs. Patients are encouraged to track their medication usage meticulously—keeping a record of inhaler puffs and doses—so that healthcare professionals can adjust treatments accordingly. Effective communication with healthcare providers allows for personalized management plans that optimize therapeutic outcomes. For allergic asthma, desensitizing allergy injections, or immunotherapy, are a promising approach that reduces sensitivity to specific allergens over time, administered typically every two to four weeks. These injections can lessen the frequency of asthma exacerbations triggered by environmental allergens.
Innovative treatments are continuously emerging in the realm of asthma care. Bronchial thermoplasty, for example, is a minimally invasive procedure that involves heating the smooth muscle tissue lining the bronchi with a specialized electrode. This process reduces airway muscle contraction and thereby diminishes the severity and frequency of asthma attacks. Although this procedure is not universally available, clinical trials and specialized centers are expanding its accessibility for suitable candidates. Alongside these therapies, technological advancements in inhaler devices are revolutionizing asthma care.
Modern inhaler technology has significantly improved medication delivery. Traditional metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) are now commonly equipped with spacers—mosquito-like extensions that make inhalation easier, especially for children and the elderly. Spacers ensure the proper dose reaches the lungs, reducing medication waste and side effects caused by improper inhalation technique. Nebulizers, another critical tool, convert liquid medication into a fine mist, ideal for patients with severe breathing difficulty or those who require larger doses of medication. They are especially useful in hospital settings or during acute attacks when rapid delivery of medication is necessary.
In conclusion, the landscape of asthma management is rapidly evolving, driven by innovations in medication delivery, procedural interventions, and personalized care strategies. Patients and healthcare providers must stay informed about the latest options to ensure optimal disease control, minimize episodes, and improve the overall quality of life. With ongoing research and technological progress, individuals living with asthma can look forward to better management techniques that are safer, more effective, and more convenient.