Comprehensive Guide to Asperger's Syndrome: Recognizing Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores Asperger's syndrome, highlighting key signs in children and adults, diagnostic methods, and effective management strategies. It aims to provide valuable insights for parents, educators, and individuals, emphasizing early intervention and support to improve social, emotional, and daily living skills for those affected by this neurodevelopmental condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Asperger's Syndrome: Recognizing Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Effective Management Strategies
Asperger's syndrome, a condition falling under the spectrum of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is characterized by unique neurodevelopmental features that primarily influence social interactions, communication, and behavioral patterns. Although individuals with Asperger's often display normal language development and average or above-average intelligence, they face distinctive challenges that can impact their personal, academic, and professional lives. Understanding the core aspects of Asperger's syndrome, including its key signs, how it is diagnosed, and what management options are available, is vital for early intervention and improved quality of life.
Recognizing Key Signs of Asperger's in Children
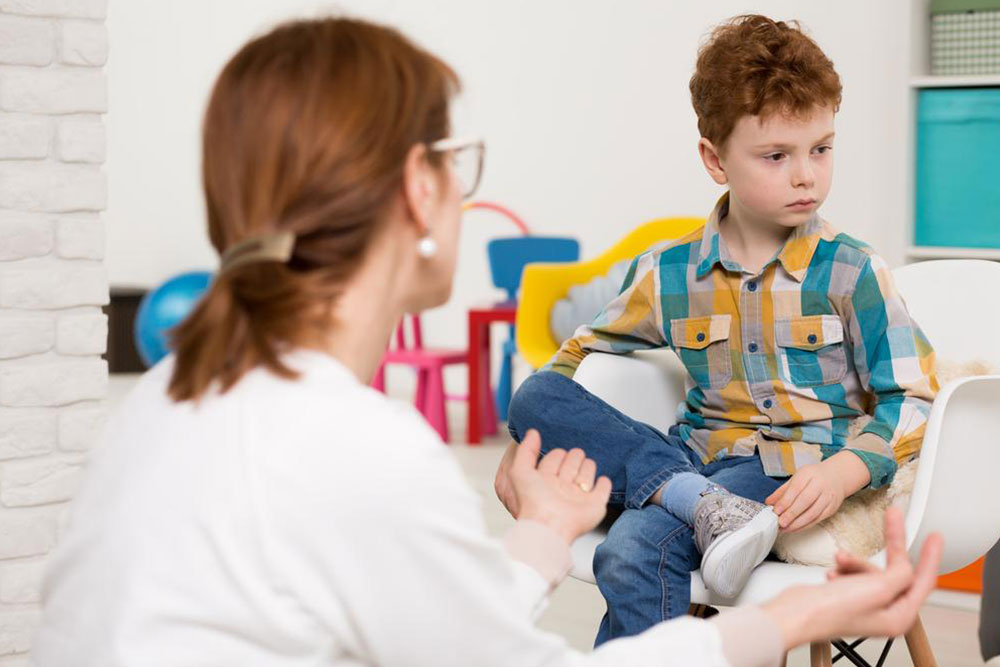
Children with Asperger's often exhibit specific behavioral traits that set them apart from their peers. One of the most prominent indicators is difficulty engaging in typical social interactions. These children may appear socially awkward, misreading social cues such as facial expressions, tone of voice, or body language. For example, they might not respond appropriately to social gestures or seem aloof and disinterested in peer activities, which can lead to social isolation.
They tend to avoid eye contact, which is often mistaken for shyness but is more indicative of sensory or social processing difficulties. Expressing emotions verbally can be challenging, with some children struggling to articulate feelings or understand others' emotional expressions. Repetitive behaviors—such as rocking, tapping, or hand-flapping—are common and serve as self-stimulation or coping mechanisms.
Enhanced sensitivities to sensory stimuli are also characteristic. Children with Asperger's might react strongly to certain sounds, textures, lights, or smells, leading to tantrums or withdrawal in overwhelming environments. This sensory processing difference can significantly interfere with daily activities.
Another hallmark feature is an intense preoccupation with specific topics or hobbies. These interests are often detailed and persistent, such as collecting certain objects, memorizing facts about a niche subject, or engaging in repetitive routines. Difficulty adapting to change or transitioning from one activity to another can cause distress, often resulting in emotional meltdowns over seemingly minor alterations.
Furthermore, children with Asperger's often display a literal understanding of language, which can lead to misunderstandings or social faux pas. They may show limited use of imaginative play and prefer solitary activities over group play, further isolating themselves socially.
It's crucial for parents, teachers, and caregivers to observe these behaviors and their impact on the child's daily life. When such behaviors cause significant distress, impede learning, or affect social relationships, seeking professional evaluation becomes essential. Early diagnosis and intervention can dramatically improve outcomes, helping children develop essential skills and navigate their environment more comfortably.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tools
Diagnosing Asperger's syndrome involves a comprehensive evaluation conducted by multidisciplinary professionals, including psychologists, developmental pediatricians, speech-language pathologists, and occupational therapists. The process typically includes detailed behavioral assessments, developmental history, and standardized testing, such as IQ tests to rule out other conditions and understand cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
Behavioral assessments are often based on criteria outlined in diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5, focusing on social communication difficulties and restrictive, repetitive behaviors. Observations from parents and teachers play a vital role, as they provide insights into the child's behavior across different settings and over time.
Additional assessments may include sensory profiling and language development evaluations to better tailor intervention strategies. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial, allowing intervention plans to be customized to meet the child's specific needs, thereby maximizing developmental progress and social adaptation.
Management and Support Strategies
There is currently no cure for Asperger's syndrome; however, a variety of therapeutic approaches can significantly enhance a person's functioning and quality of life. The focus is on developing social, communication, and adaptive skills while providing support for sensory challenges and behavioral issues.
Behavioral therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), helps modify maladaptive behaviors and reinforce positive social interactions. Social skills training groups teach children practical skills like turn-taking, understanding social cues, and sharing interests, which can improve peer relationships.
Occupational therapy addresses sensory processing issues and helps develop daily living skills such as dressing, grooming, and organization. Speech therapy can improve language pragmatics, helping individuals better interpret social language and express themselves more effectively.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in managing Asperger's. Education on the condition, along with strategies for managing meltdowns or sensory overloads, empowers families to create supportive environments. Joining support groups provides emotional solidarity, practical advice, and advocacy opportunities.
Consistency and routine are important for individuals with Asperger's, helping reduce anxiety and increase predictability. Visual aids and social stories can be effective tools to teach expected behaviors and prepare them for changes or new experiences.
Early intervention is critical. The sooner support begins, the greater the likelihood of improving social skills, academic performance, and independence. Regular follow-ups and adapting strategies to the individual's evolving needs ensure sustained progress.
Recognizing Asperger's in Adults
While often diagnosed in childhood, many adults with Asperger's remain undiagnosed or are diagnosed later in life. Adults with Asperger's tend to excel in specialized fields that require attention to detail, analytical thinking, or technical skills. However, they may face ongoing challenges in social communication and forming meaningful relationships.
Typical signs in adults include difficulty interpreting nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Conversation may seem monotonous or one-sided, with a tendency to focus intensely on specific interests or topics. An adult with Asperger's might prefer routines and dislike disruptions, leading to anxiety in unpredictable situations.
Emotionally, some adults report feeling isolated or misunderstood, despite successful professional lives. They might display rigid thinking patterns or experience discomfort in social settings that require nuanced social understanding. Recognizing these traits can help in seeking support or accommodations that improve daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.