Ultimate Guide to Managing Scabies Infestation and Its Skin Reactions
This comprehensive guide dives into the causes, symptoms, treatments, and natural remedies for managing scabies and its associated skin reactions. It emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis and professional medical intervention while also exploring effective home remedies to soothe symptoms. Whether for adults, children, or severe cases, this article provides valuable insights to address scabies safely and effectively, facilitating better skin health and reducing contagion risks.

Comprehensive Understanding of Scabies and Its Skin Manifestations
Introduction to Scabies and Its Skin Symptoms
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. Unlike many skin infections, scabies results from an allergic reaction to the mite's presence and its burrowing activity beneath the outermost layer of skin. This infestation is characterized by intense itching, especially at night, and distinctive skin rashes. It is essential to understand that scabies is transmitted through prolonged, close physical contact, including sexual contact, sharing bedding, clothing, or towels. Adults often showcase visible signs like burrow tracks and rashes, which can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions but are distinguishable upon clinical examination and images available online.
Signs and Symptoms of Scabies
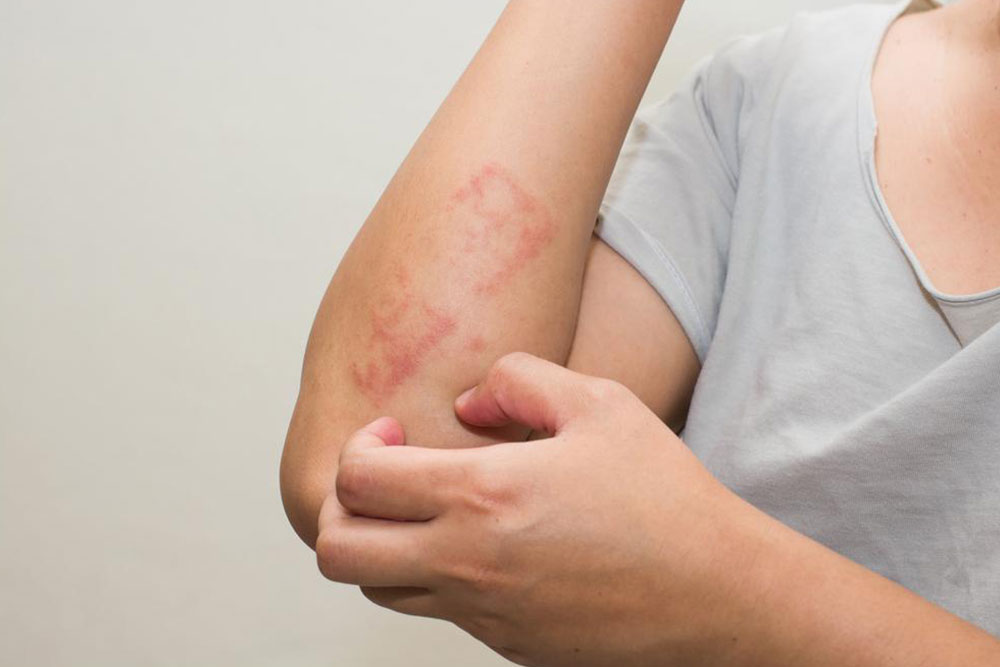
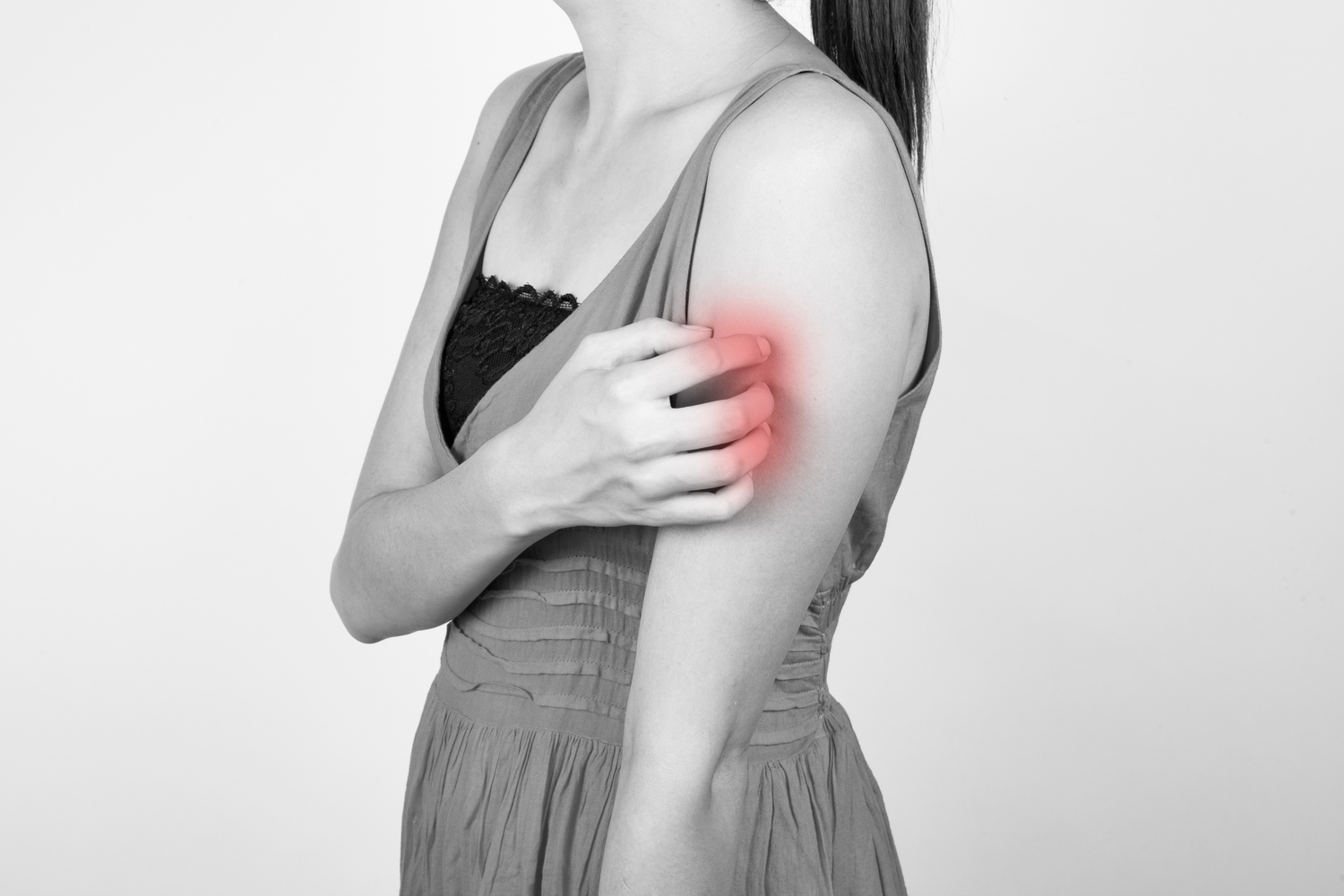
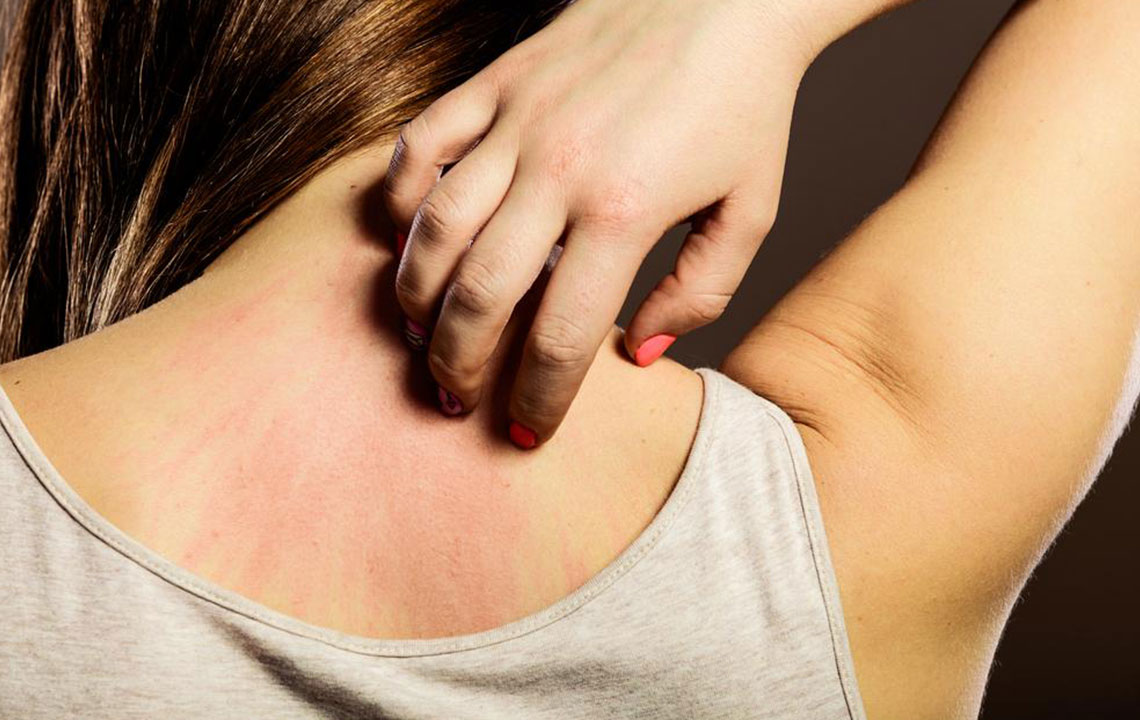
Severe Itching: The hallmark symptom of scabies is persistent itching, which becomes more intense during nighttime, causing significant discomfort and disturbed sleep.
Burrow Tracks: These appear as thin, wavy, thread-like lines on the skin surface, often accompanied by flaky skin patches, blisters, or papules. They can be visualized in clinical images for accurate identification.
Skin Damage from Scratching: Persistent scratching leads to open sores, crusted scabs, and sometimes secondary bacterial infections such as impetigo, which require additional treatment.
Thickened and Crusted Skin: In severe cases, especially in immunocompromised individuals, the skin becomes thickened, crusted, and hyperkeratotic, a condition known as crusted or Norwegian scabies.
Effective Medical Treatments for Scabies
Topical Medications: Permethrin 5% cream (Elimite) remains the first-line treatment. It is applied thoroughly over the entire body surface from the neck down, preferably after bathing and thorough cleaning of nails and skin. Leave it on for 8-14 hours before washing off. Reapplication is typically necessary after a week to ensure all mites, including eggs, are eradicated.
Alternative Topical Agents: Benzyl benzoate, sulfur ointments, and crotamiton are traditional options. However, due to potential skin irritation and lower efficacy, they are less favored in current practice.
Systemic Therapy: Ivermectin oral pills are effective for widespread or crusted scabies, especially in cases resistant to topical therapies. It is usually administered as a single dose, with a repeat dose after 7-14 days if necessary, under healthcare supervision.
Other Treatments: Lindane 1% may be used in some cases but is avoided due to neurotoxicity risks, especially in children and pregnant women.
Common Areas of Infestation
In Adults and Older Children: Mites frequently inhabit the interdigital spaces of fingers, wrists, underarms, waistline, nipples, genital regions, knees, and shoulder blades. These areas are prone to visible rashes and burrows, which can be confirmed via clinical images and dermatological examination.
In Infants and Young Children: The infestation often affects the scalp, face, palms, and soles of the feet, areas less commonly involved in adults. These manifestations are often visible and require close inspection, aided by high-quality images for diagnostic purposes.
Home Remedies and Natural Approaches to Manage Symptoms
Tea Tree Oil: Known for its natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, tea tree oil can diminish itching and rash severity. To use, dilute with a carrier oil and apply topically or add a few drops to bedding and clothing to help reduce mite presence.
Neem Oil: This oil exhibits potent anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antiparasitic properties that can effectively combat mites and soothe irritated skin.
Aloe Vera Gel: Widely used for its cooling, healing, and anti-inflammatory effects, aloe vera can alleviate itching and promote skin repair.
Cayenne Pepper: When used cautiously, cayenne pepper can desensitize nerve endings, reducing discomfort. It can be prepared as a topical paste or used in dietary practices for added benefits.
Clove Oil: With its natural antimicrobial and insecticidal properties, clove oil can serve as an alternative remedy to control mite infestation and promote skin health.
Strategies for Itching Relief and Symptom Management
Cooling Therapies: Taking cool water baths or applying cool compresses to affected areas can significantly reduce itching and inflammation.
Moisturizers and Topical Soothers: Calamine lotion, aloe vera gel, or other soothing emollients provide temporary relief from itching.
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines like cetirizine or diphenhydramine can help lessen allergic responses and reduce itching, but they do not treat the infestation itself.
Medical Consultation: A healthcare professional should be consulted before initiating any treatment plan. They can prescribe appropriate medications and provide guidance tailored to individual cases.
In conclusion, an accurate diagnosis combined with effective medication and holistic care approaches is essential for eliminating scabies and alleviating associated skin reactions. Proper treatment minimizes discomfort and prevents the spread of this contagious condition, ensuring a swift recovery and healthier skin.