Comprehensive Guide to Bladder Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into bladder infections, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and preventive strategies. Learn how to recognize early signs, understand risk factors, and adopt effective preventive measures to maintain urinary health. The article covers essential treatments and lifestyle tips to help individuals manage and avoid these common infections, emphasizing the importance of hygiene, hydration, and medical consultation for persistent symptoms. Stay informed to protect your urinary health effectively.
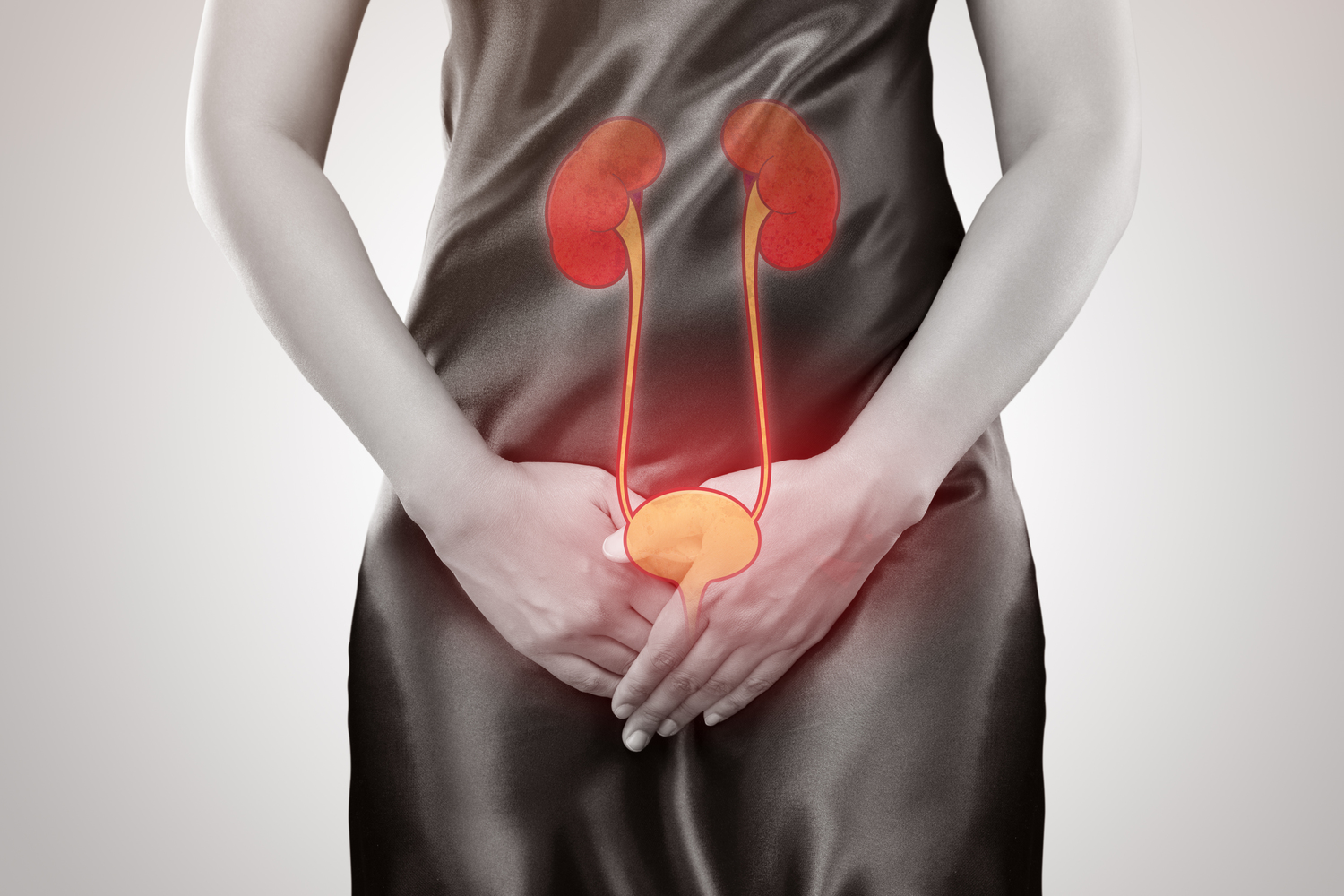
Comprehensive Guide to Bladder Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Strategies
Bladder infections, a prevalent form of urinary tract infection (UTI), pose significant health concerns worldwide. These infections occur when bacteria invade the bladder lining, leading to discomfort, pain, and potential complications if left untreated. The most common bacterial culprit responsible for bladder infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which naturally resides in the human intestines. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of bladder infections by exploring their causes, characteristic symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, available treatments, and practical prevention tips.
Gain detailed insights into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and preventative measures for bladder infections to better manage and avoid these common ailments.
Understanding the Causes of Bladder Infections
Typically, bacteria like E. coli that are present in the intestinal tract are usually eliminated from the urinary system through urination.
Infections happen when these bacteria ascend from the urethra into the bladder, where they multiply and establish an infection.
If unchecked, bacteria can ascend further to infect the kidneys, potentially leading to more serious health issues such as pyelonephritis.
Women are more susceptible because their urethra is anatomically closer to the anus, allowing easier bacterial transfer.
Other factors, such as immune system suppression and certain health conditions like diabetes, can elevate the risk of infection.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Bladder Infections
Persistent a burning sensation or pain during urination, often accompanied by discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Urine may appear cloudy, dark, or contain traces of blood, indicating infection.
Increased frequency of urination, sometimes with an urgent need to urinate even when the bladder isn't full.
Strong foul odor emanating from urine, a common sign of bacterial presence.
In severe cases, patients may experience back pain, chills, fever, and nausea, symptoms hinting at possible kidney involvement.
Risk Factors Contributing to Bladder Infections
Engaging in sexual activity, particularly with new or multiple partners, increases susceptibility.
Not urinating after sexual intercourse can facilitate bacterial transfer into the urinary tract.
Older adults, especially women entering menopause, experience hormonal changes that affect urinary tract defenses.
Chronic health conditions such as diabetes impair immune responses, heightening infection risk.
Use of certain contraceptive methods like diaphragms with spermicide can predispose women to UTIs.
Other behaviors, including poor personal hygiene and dehydration, also play a role.
How Bladder Infections Are Diagnosed
Laboratory analysis of urine samples to detect bacteria, white blood cells, blood, or pus helps confirm infection.
Imaging techniques like ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRI may be employed if the infection involves the kidneys or if there are recurrent episodes.
A cystoscopy, which involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the urethra, allows for direct visualization of the bladder interior and tissue sampling if necessary.
Effective Treatment Options for Bladder Infections
Most uncomplicated bladder infections resolve naturally within a few days, though medical intervention can expedite recovery.
Antibiotics constitute the primary treatment, with durations ranging from a single dose to several weeks, depending on infection severity.
Topical or vaginal creams may be prescribed to relieve irritation or discomfort.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and cramps.
Applying warm compresses or hot water bottles on the lower abdomen can provide additional pain relief.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Bladder Infection Risk
Maintain proper hydration by drinking plenty of water throughout the day to help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Avoid bladder irritants like spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol that can worsen symptoms.
Refrain from using artificial sweeteners, which can irritate the bladder mucosa.
Consuming cranberry juice or supplements has been shown to inhibit bacterial adhesion, especially E. coli, to the urinary tract lining.
Use gentle, unscented soaps and avoid feminine hygiene sprays that can disrupt natural flora and cause irritation.
Always wipe from front to back after urination or defecation to prevent bacterial transfer to the urethra.
Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing to promote airflow and reduce moisture buildup.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and adopting appropriate preventive practices are crucial steps in managing bladder infections effectively. If symptoms persist or recur frequently, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing bladder infections and maintain a healthy urinary system.





