Complete Dietary Strategies for Managing Gout Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective dietary strategies to manage gout, emphasizing foods to include and avoid, hydration tips, and flavorful recipes. Learn how to control uric acid levels naturally, reduce flare-ups, and maintain an enjoyable, healthy diet tailored to gout sufferers, all while focusing on balanced nutrition and lifestyle modifications.

Complete Dietary Strategies for Managing Gout Effectively
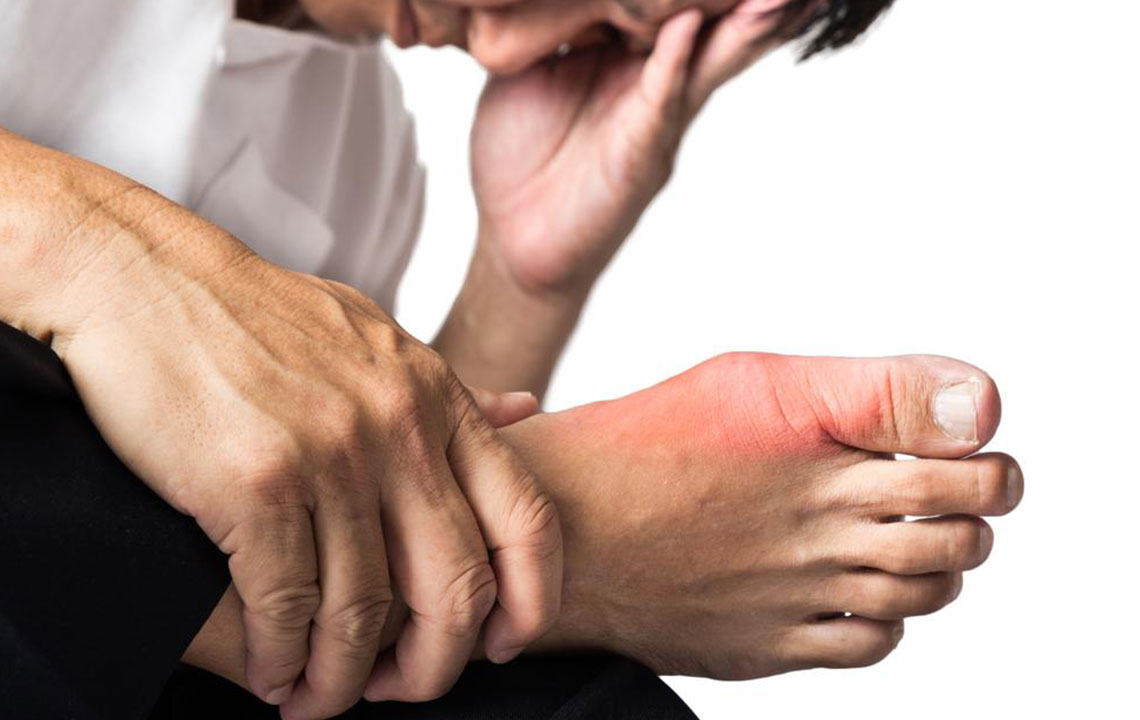
Gout is a complex and often intensely painful form of arthritis that predominantly affects the big toe but can also involve other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows. It is characterized by sudden, sharp, and burning pain due to inflammation caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals within joint tissues. Managing gout requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, particularly dietary changes, to control uric acid levels and reduce flare-ups.
Understanding the Causes of Gout
Gout develops when the body produces excessive uric acid or fails to eliminate it efficiently. Normally, uric acid is a waste product generated during the breakdown of purines—substances found naturally in our bodies and in many foods. When uric acid levels become elevated, crystals form and deposit in the joints, triggering inflammation and intense pain. Various factors can contribute to hyperuricemia, including genetics, obesity, certain medications, dehydration, and dietary habits.
Role of Purines and Diet in Gout Management
Purines are organic compounds found in many foods, and their breakdown produces uric acid. While purines are essential for functions like DNA synthesis, high dietary purine intake can elevate uric acid levels, increasing the risk of gout attacks. Historically, dietary guidelines emphasized reducing purine-rich foods, especially organ meats and certain types of seafood. However, recent research sheds light on the nuanced relationship between purines and gout, suggesting that some high-purine vegetables might not exacerbate symptoms and could provide beneficial nutrients that help decrease crystal formation and inflammation. This evolving understanding allows for more balanced dietary strategies that do not overly restrict nutrient-rich vegetables.
Developing an Anti-Gout Diet Plan
Effective gout management involves adopting an anti-inflammatory and uric acid-lowering diet tailored to individual needs, along with maintaining healthy weight and hydration levels. Here are key dietary principles to help control gout:
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight significantly raises uric acid levels and puts additional stress on joints. Losing even a modest amount of weight can dramatically reduce the risk of gout attacks and alleviate joint pain. Incorporate balanced nutrition combined with regular physical activity to achieve and sustain a healthy weight.
Stay Well-Hydrated
Proper hydration plays a crucial role in flushing uric acid from the body. Drinking plenty of water—aiming for at least 8-10 glasses daily—can help prevent crystal formation and decrease attack frequency. For personalized recommendations, consult your healthcare provider about optimal fluid intake based on your health status.
Incorporate Complex Carbohydrates
Replacing refined sugars and processed snacks with fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports digestion and enhances detoxification. Complex carbohydrates help stabilize blood sugar levels and can play a role in lowering uric acid levels.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, can elevate uric acid levels and promote crystal formation. Beer is especially problematic as it contains high purines derived from yeast. Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining completely can significantly reduce gout flare-ups.
Avoid High-Purine Foods
Reduce intake of foods known to have high purine content, including organ meats (liver, kidneys), red meats (beef, lamb), shellfish (shrimp, crab), and fatty fish like sardines, anchovies, and tuna. Additionally, minimize consumption of high-fat dairy products, sugary beverages, and processed foods that can trigger inflammation.
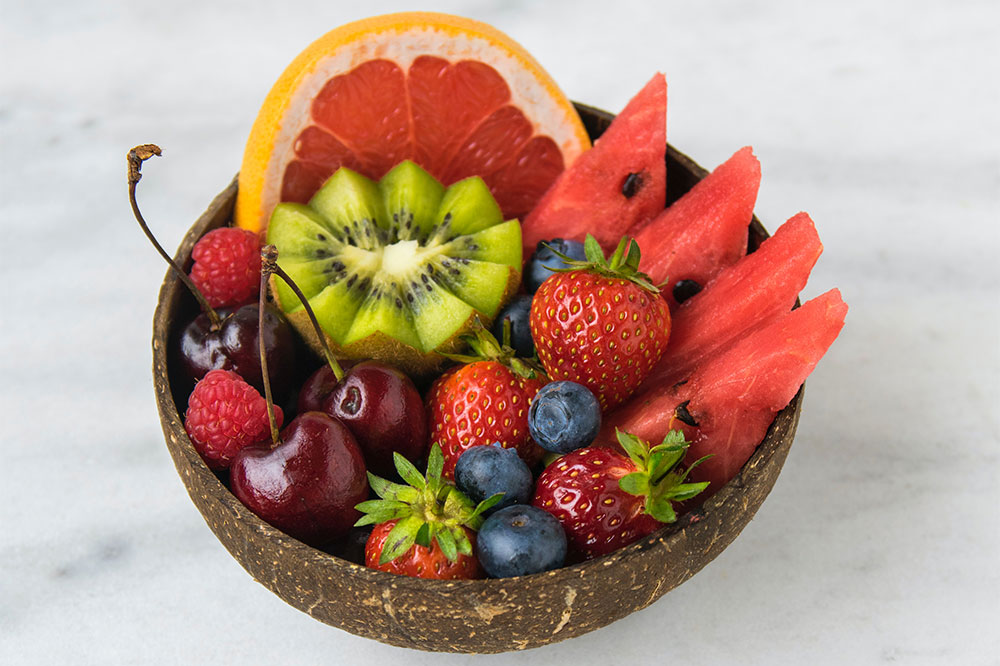
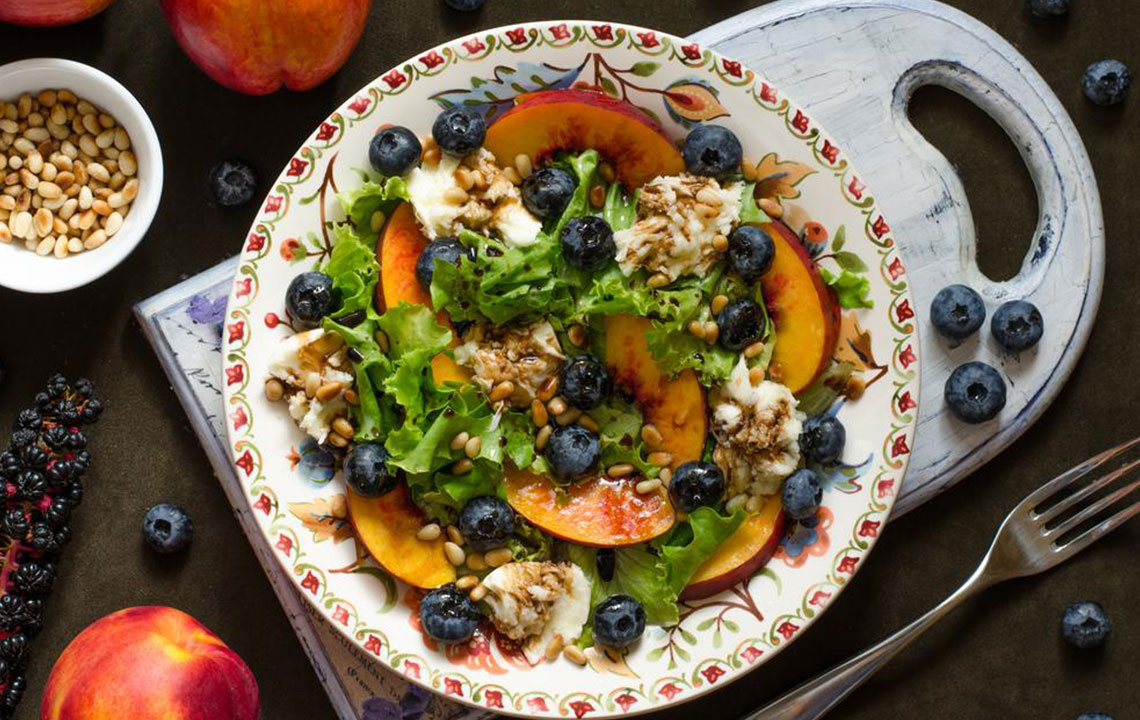
Choose Gout-Fighting Fruits and Vegetables
Vegetables such as spinach, asparagus, and mushrooms, even though high in purines, are generally safe as they contain compounds that may counteract purine effects. Fruits like cherries, berries, and citrus are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help prevent attacks. Cherries, in particular, have been shown in numerous studies to reduce gout episodes by over 50% with regular intake.
Enjoy Coffee in Moderation
Moderate coffee consumption has been linked with decreased uric acid levels and a lower risk of gout. The polyphenols in coffee may contribute to their protective effect. However, always consult your healthcare professional regarding caffeine intake, especially if you have other health conditions.
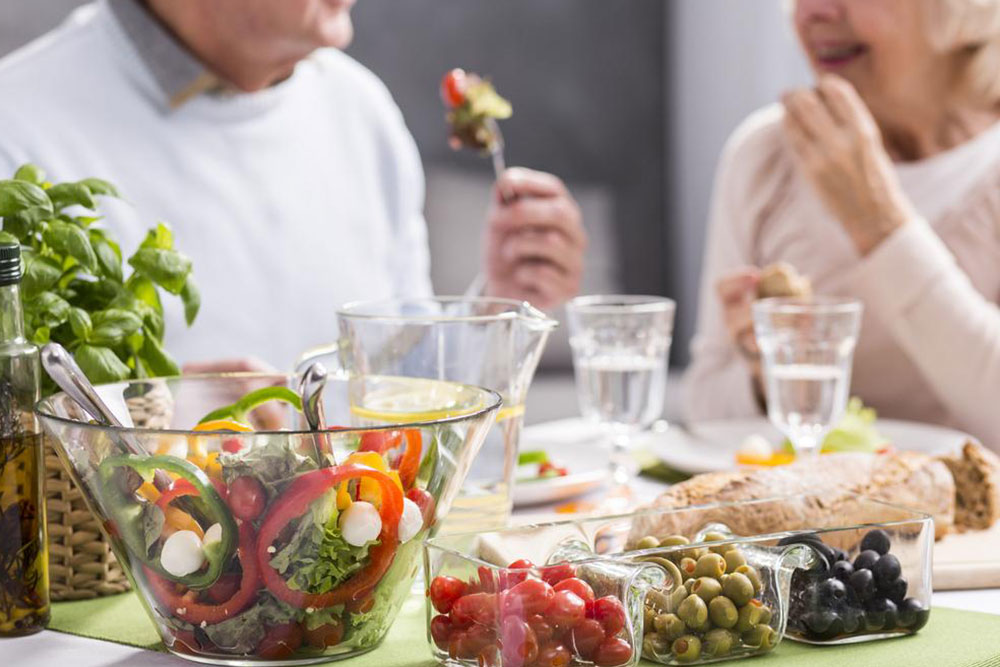
Creating Delicious and Safe Gout-Friendly Meals
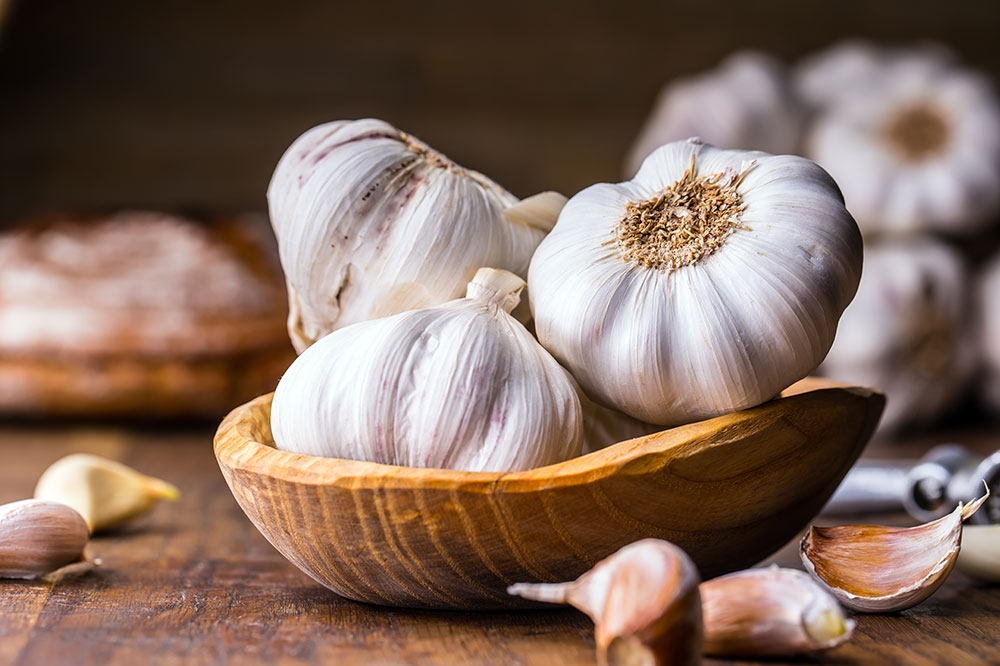
Concerns about bland or boring food are common among those managing gout. The good news is that there are countless flavorful recipes and meal ideas designed to be both tasty and safe for gout sufferers. Incorporating herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, garlic, basil, and oregano can add flavor without increasing purine content. For example, try preparing spicy vegetable stir-fries, herb-marinated grilled chicken or fish, hearty vegetarian pastas, or Mediterranean-inspired salads. Experimenting with different cuisines and cooking methods can help make your diet enjoyable and sustainable.
Achieving a gout-friendly diet doesn't mean sacrificing taste. Through careful planning and culinary creativity, you can enjoy delicious, nutritious, and anti-inflammatory meals that support your health, reduce pain episodes, and enhance overall well-being.