Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Complete Guide
This comprehensive guide covers everything about advanced prostate cancer, including its progression, symptoms, and a wide range of treatment options such as radiation, chemotherapy, surgery, and targeted therapies. Understanding these aspects helps patients and caregivers make informed decisions and improve quality of life during treatment.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Complete Guide
Discovering that you have advanced prostate cancer can be overwhelming and raise numerous concerns about treatment options, prognosis, and quality of life. Navigating the complexities of this disease requires thorough understanding and informed decision-making. This detailed guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into advanced prostate cancer, including its progression, symptoms, and the wide array of available treatments. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or simply seeking knowledge, understanding these aspects empowers you to make informed choices and prepare for the road ahead.
Understanding the Progression of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men worldwide. Its progression is typically categorized into localized, locally advanced, and metastatic stages. When prostate cancer begins to extend beyond the confines of the prostate gland into nearby lymph nodes, bones, or other tissues, it is classified as advanced. This stage signifies that the cancer has grown beyond the initial site, making treatment more complex and demanding multiple approaches.
In cases where the cancer spreads further to distant parts of the body, such as lungs, liver, or other organs, it is termed metastatic prostate cancer. The management of metastatic prostate cancer focuses not only on controlling tumor growth but also on alleviating symptoms and maintaining the quality of life. Understanding the extent of disease spread through diagnostic imaging and blood tests is crucial to plan effective treatment strategies.
Recognize the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Early detection of prostate cancer can significantly influence treatment success and outcomes. Some men may experience subtle symptoms, while others notice more pronounced signs as the disease advances. Recognizing these symptoms promptly and seeking medical advice is vital for early intervention.
Common signs associated with advanced prostate cancer include:
Urinary Difficulties: An enlarged prostate can cause symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, weak or interrupted stream, or a frequent need to urinate, especially at night. These signs may be indicative of local tumor growth pressing on the urethra.
Changes in Blood Count: Weakness, fatigue, or pallor may develop due to anemia caused by disrupted red blood cell production, often linked to bone marrow involvement or chronic disease effects.
Bone Pain and Fractures: When prostate cancer metastasizes to bones, patients might experience persistent bone pain, tenderness, or fractures caused by weakened bones.
Hematuria and Hematospermia: Blood in the urine or semen can signal tumor invasion into the urinary tract or seminal vesicles.
Pain During Erection or Ejaculation: Discomfort or pain during sexual activity may indicate local tumor invasion or nerve involvement.
Sexual Dysfunction: Erectile problems or reduced libido can sometimes be associated with hormonal therapy or disease progression.
Timely recognition of these symptoms and consultation with a healthcare professional, especially a urologist or oncologist, are critical steps towards diagnosis and treatment.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for Advanced Prostate Cancer
Managing advanced prostate cancer involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific disease characteristics, overall health, and personal preferences. Advances in medical technology and therapeutic options have significantly expanded treatment possibilities, offering hope and improved quality of life for patients.
Key treatments include:
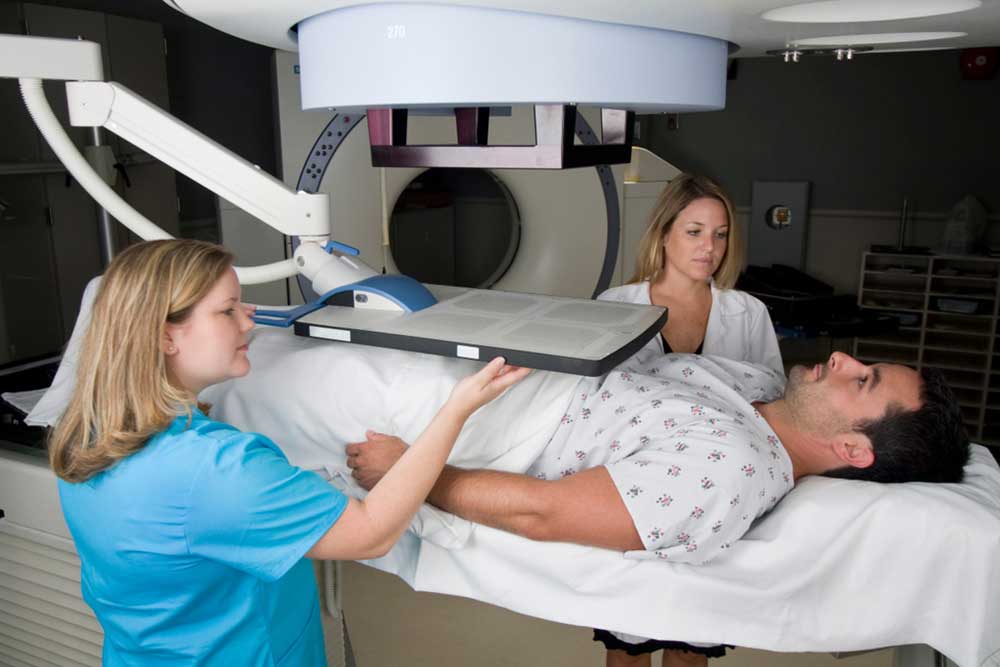
Radiation Therapy: Utilizes high-energy rays to target and destroy malignant cells within the prostate or metastatic sites. Techniques such as external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) are commonly used.
Chemotherapy: Employs potent drugs to kill or inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells. It is particularly useful in cases where the disease has spread widely or resistant to hormone therapy.
Surgical Interventions: Radical prostatectomy, the complete removal of the prostate gland, may be considered in select cases, especially when the tumor is localized or has limited spread.
Brachytherapy: Involves implanting radioactive seeds directly into the prostate to deliver localized radiation doses, effectively reducing tumor size and controlling disease progression.
Cryosurgery: This minimally invasive procedure freezes and destroys cancerous tissues, providing an alternative treatment option with fewer side effects.
Hormonal Therapy: Inhibits testosterone production or blocks its effects, which is crucial because prostate cancer growth is often hormone-dependent. Drugs such as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists/antagonists and anti-androgens fall under this category.
Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapies: Advanced treatments like high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) aim to destroy cancer cells precisely, while immunotherapies help stimulate the body's immune response against cancer.
Emerging Treatments: Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as gene therapy, vaccine therapy, and combination treatments to improve outcomes further.
Deciding on the most appropriate treatment requires careful evaluation by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals. Factors influencing the choice include tumor size and location, metastasis extent, patient age, comorbid conditions, and personal preferences. Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for developing a tailored treatment plan that aligns with your goals and expectations.
Quality of life considerations, including managing side effects and preserving functions like sexual health, are integral parts of the treatment planning process. Supportive care, including pain management, nutritional support, and psychological counseling, can significantly enhance well-being during treatment.
In conclusion, managing advanced prostate cancer is a complex process but one that has been greatly improved through ongoing research and technological innovation. By understanding the progression, symptoms, and comprehensive treatment options, patients and their families can navigate this challenging journey more confidently and effectively.