Essential Insights into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment, and Care Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores breast cancer, from understanding its types and early signs to advanced diagnostic methods and cutting-edge treatment options. Emphasizing early detection and personalized therapies, it aims to inform patients and healthcare providers about the latest developments in managing this prevalent disease. Early intervention remains key to improving survival rates, and ongoing research offers hope for more effective treatments in the future. Stay informed to protect your breast health and optimize treatment outcomes.

Comprehensive Understanding of Breast Cancer: Detection, Diagnosis, and Therapy Options
Introduction to Breast Cancer
"Never underestimate the importance of early detection." Breast cancer is undeniably one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide and can also impact men, although less frequently. Over recent decades, significant advancements have been achieved in awareness campaigns, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Early detection remains the cornerstone of effective management, significantly improving prognosis and survival rates. The development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine has revolutionized treatment approaches, especially for metastatic breast cancer, offering new hope for patients. Ongoing research continues to unveil innovative solutions, paving the way for more effective and less invasive treatments.
What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer ranks as the second most common cancer among women globally, accounting for roughly 12% of all female cancers.
This disease develops when abnormal, malignant cells grow within the breast tissues, which can occur in any part of the breast, including ducts, lobules, or surrounding tissues.
In men, although less prevalent, breast cancer can also occur, highlighting that both genders should be vigilant about breast health.
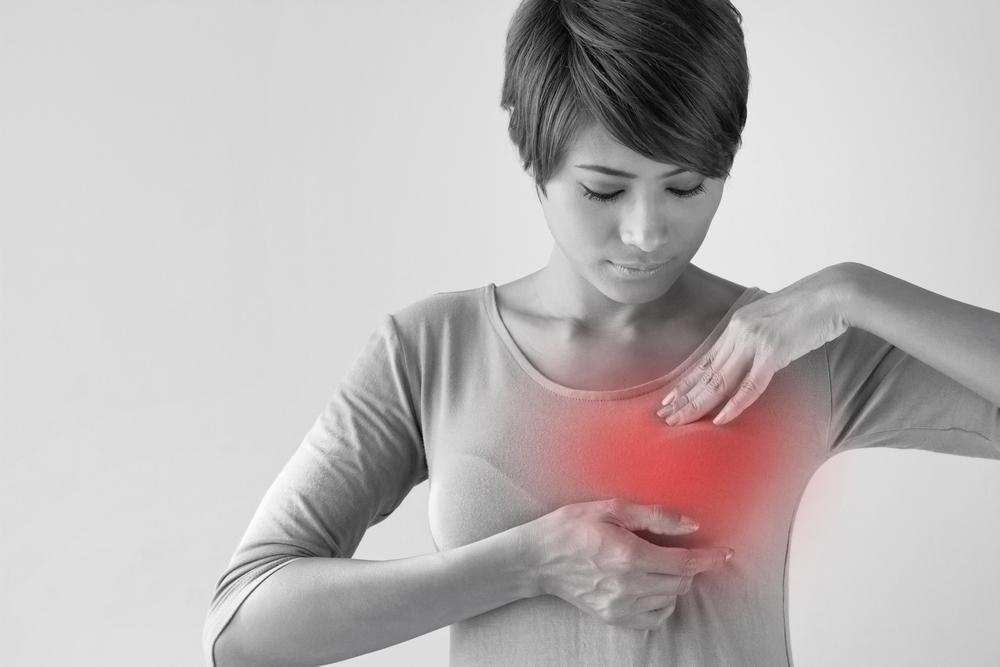
Early Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
Being aware of the early symptoms is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. Regular self-examination from a young age can greatly aid early detection.
Any persistent or unusual changes in the breast or nipple should prompt immediate consultation with healthcare professionals. It is important to differentiate between normal cyclical breast changes and signs of potential problems.
Watch for skin alterations such as redness, dimpling, or puckering; nipple retraction or inversion; the presence of scales or flakes around the areola; or palpable lumps that differ from normal breast tissue.
If metastasis occurs, symptoms depend on the affected organs, commonly including neurological symptoms if the brain is involved, respiratory issues with lung involvement, bone pain, or signs of liver dysfunction.
Diagnostic Procedures for Breast Cancer
Initial assessment involves physical exams focusing on the breasts and surrounding lymph nodes, especially in the armpits, to detect any abnormal masses or swelling.
Imaging techniques such as mammograms, ultrasounds, and MRI scans are essential tools for detecting suspicious areas within the breast tissue.
In addition, core needle biopsies—guided by imaging—are performed to obtain tissue samples for histopathological examination. Markers or clips are often placed during biopsy to identify sampled areas for future reference.
The analysis of biopsy samples determines the exact type, grade, and stage of cancer, critical for developing a personalized treatment plan.
Types and Classifications of Breast Cancer
Angiosarcoma, though rare, affects the lining of blood vessels and lymph vessels within the breast tissue.
DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma in Situ) is an early-stage, non-invasive cancer confined within the milk ducts, with a minimal risk of spreading.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a highly aggressive form characterized by swelling, redness, warmth, and a peau d’orange skin texture.
Invasive lobular carcinoma originates in the milk-producing lobules and can invade surrounding tissues or metastasize to other parts of the body.
Male breast cancer, though rare, emphasizes that men are not immune and require awareness and timely investigation.
Paget’s disease affects the nipple and spreads to the areola, often associated with underlying ductal carcinomas.
Recurrent breast cancer indicates a recurrence after initial treatment, often suggesting resistance to therapy or persistent disease.
Management and Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Significant progress has been made with surgical techniques, systemic therapies, and the advent of targeted treatments, improving patient outcomes and cosmetic results.
Testing for hormone receptors such as estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PR) helps clinicians tailor hormone therapy, reducing tumor size pre-surgery and minimizing recurrence risks.
Current therapeutic strategies include mastectomy, lumpectomy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, and novel targeted agents designed to interfere with specific molecular pathways.
Emerging treatments focus on precision medicine approaches, utilizing cutting-edge molecules and immune-modulating therapies to combat resistant or advanced disease.
In summary, breast cancer remains a complex disease requiring a multidisciplinary approach. Advances in early detection, diagnostic accuracy, and personalized treatments continue to enhance patient survival and quality of life. Staying informed and proactive about breast health is essential for early diagnosis and effective management, ultimately saving lives and reducing the disease's burden across populations.