In-Depth Guide to Understanding and Managing Fibromyalgia
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth understanding of fibromyalgia, including its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle adjustments, alternative therapies, and dispelling misconceptions to improve patient outcomes and awareness of this complex condition.

Comprehensive Understanding of Fibromyalgia
Introduction to Fibromyalgia
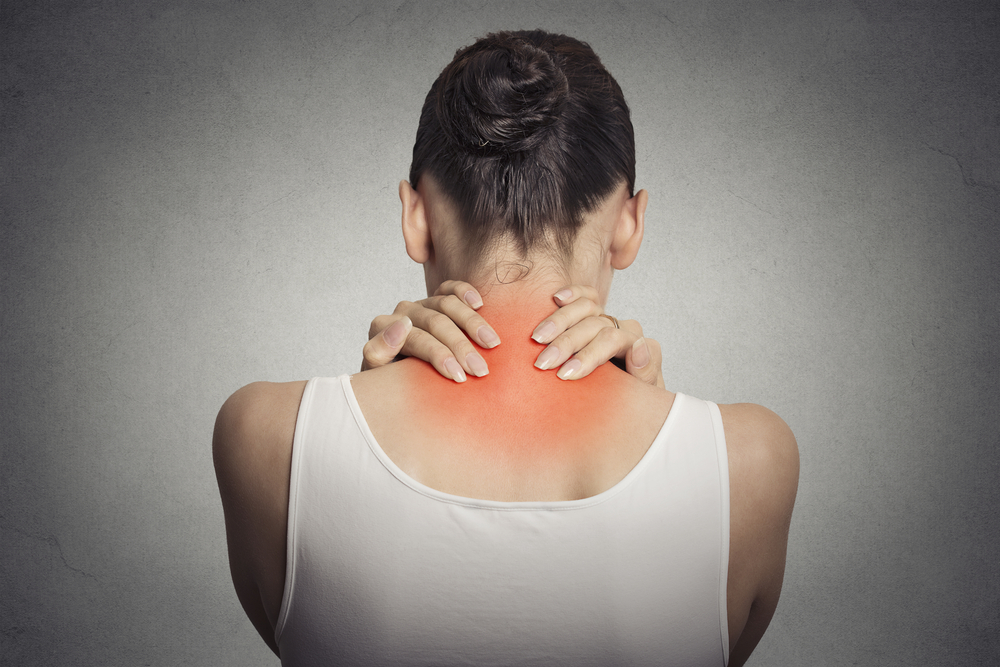
Fibromyalgia is a complex, long-term condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and a range of other symptoms. It often challenges both patients and healthcare providers due to its subjective nature and the difficulties involved in diagnosing it accurately. Many individuals with fibromyalgia experience persistent muscle tenderness, exhaustion, and cognitive disturbances, which can significantly impair daily functioning. Its elusive cause and diverse symptoms sometimes lead to misdiagnosis, often mistaken for other disorders.
In this extensive guide, we delve into what fibromyalgia is, explore its potential causes, review common symptoms, and discuss effective management and treatment strategies. Whether you're a patient seeking clarity or a healthcare professional looking to broaden your understanding, this comprehensive resource aims to provide valuable insights into this often misunderstood condition.
Potential Causes and Risk Factors
Despite extensive research, the exact origins of fibromyalgia remain unknown. However, multiple factors are believed to contribute to its development. Understanding these elements can aid in better management and may provide clues for future treatments. Key potential causes and risk factors include:
Infections and Illnesses: Some studies suggest that recent infections or viral illnesses can trigger or aggravate fibromyalgia symptoms. For instance, post-viral syndromes may play a role in some cases.
Trauma: Physical injuries, severe accidents, or emotional trauma can increase the risk of developing fibromyalgia. Trauma may alter how the nervous system processes pain signals, leading to heightened sensitivity.
Genetic Disposition: A family history of fibromyalgia or related disorders indicates a genetic predisposition. Certain genetic markers may influence susceptibility, making some individuals more prone to developing the condition.
Chronic Stress: Persistent mental or emotional stress impacts hormonal balance and immune functioning, potentially leading to or worsening fibromyalgia symptoms. Stress-related hormonal dysregulation can sensitize pain pathways in the nervous system.
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs
Fibromyalgia manifests through a variety of symptoms, often overlapping with other conditions. Recognizing these signs early can help in timely diagnosis and management. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Persistent Muscle and Joint Pain: Widespread tender points and soreness that do not respond to usual treatments
Extreme Fatigue: Feeling overwhelmingly tired even after adequate rest
Sleep Disturbances: Difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep, often accompanied by non-restorative sleep
Cognitive Impairment ("Fibro Fog"): Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mental sluggishness
Emotional Disorders: Elevated levels of depression or anxiety, sometimes linked to the ongoing pain and fatigue
Morning Stiffness: Stiffness that persists upon waking, often improving with movement
Headaches and Migraines: Chronic or episodic headaches that may intensify symptoms
Digestive Issues: Such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which frequently co-occurs
Menstrual Discomfort: Increased severity of menstrual pain and symptoms
Numbness or Tingling: Sensations in limbs or extremities, indicating nerve hypersensitivity
Managing Fibromyalgia: Lifestyle and Self-Care Approaches
While fibromyalgia currently has no cure, a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices can significantly improve quality of life. Tailoring an integrative approach is often most effective.
Prioritize Quality Sleep: Establishing regular sleep routines and creating a restful environment can help reduce fatigue and improve pain levels. Techniques like maintaining a sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine before bedtime, and using relaxation exercises can be beneficial.
Engage in Gentle Physical Activity: Regular low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling help increase muscle strength, flexibility, and reduce pain and fatigue. It's essential to start slowly and gradually build intensity under medical supervision.
Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress exacerbates symptoms. Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, warm baths, and mindfulness meditation can promote relaxation and mental health.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional medicine, many patients find relief through alternative therapies. These can be used alongside standard treatments to enhance symptom control.
Acupuncture: Targeted stimulation of specific points on the body can improve blood flow, reduce pain, and promote overall relaxation.
Yoga and Tai Chi: These gentle mind-body practices combine movement, breathing exercises, and meditation to ease physical tension and improve mental clarity.
Massage Therapy: Soft tissue manipulation relieves muscle tightness, reduces stress, and encourages the body’s natural painkiller production, thus helping in symptom management.
Debunking Common Myths about Fibromyalgia
Misconceptions about fibromyalgia persist, leading to misunderstandings and stigma. Clearing up these myths can foster better awareness and empathy:
Myth: It’s Not a Real Medical Condition: Fibromyalgia is a recognized medical disorder by major health authorities and involves complex changes in the nervous system that create a genuine pain experience.
Myth: There Is No Treatment: Though there is no cure currently, many treatments exist that help manage and alleviate symptoms effectively.
Myth: Only Women Are Affected: While it predominantly affects women, men can also develop fibromyalgia. Awareness of this fact is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.