Complete Guide to Leg Muscle Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for leg muscle pain. It guides readers on when to seek medical help and offers practical tips for managing and preventing discomfort, emphasizing the importance of proper care to maintain leg health and mobility.

In-Depth Understanding and Solutions for Leg Muscle Discomfort
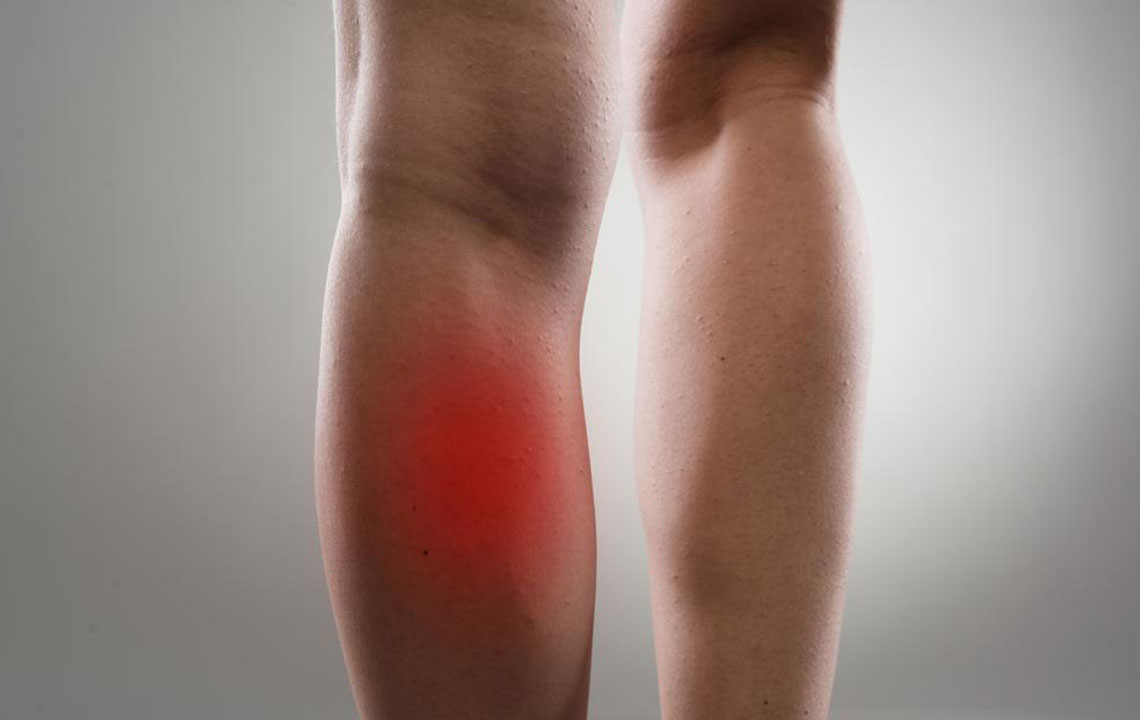
Experiencing discomfort or pain in your leg muscles can be a concerning issue, often indicating underlying health problems involving muscles, bones, joints, nerves, blood vessels, or skin. Leg muscle pain can manifest in various regions, including the ankle, thigh, behind the knee, foot, or the back of the leg. Such pain can occur during rest, physical activity, or walking, and may involve one or both legs depending on the root cause. Typically, muscle pain stems from inflammation triggered by injuries, overexertion, or certain health conditions. Recognizing the nature of your symptoms is crucial for determining whether medical consultation is necessary.
The anatomy of the leg is intricate, comprising multiple muscles, bones, nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues. This complexity means there are numerous potential causes of discomfort, ranging from minor strains to serious medical conditions. Identifying specific symptoms can aid in distinguishing between benign issues like muscle fatigue and more serious concerns such as nerve compression or circulatory problems.
Knowing when to seek prompt medical attention is essential to prevent complications. Consider consulting a healthcare professional if you notice any of the following symptoms:
Muscle cramps: Sudden, forceful contractions often caused by dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue, overuse, or poor circulation can be intensely painful and disrupt daily activities.
Severe cramps can cause significant discomfort, sometimes accompanied by muscle stiffness or weakness.
Swelling and inflammation: Pain accompanied by swelling, redness, or warmth around the muscle may indicate injury, muscle strain, or even infection.
Difficulty walking or limping: Persistent pain that hampers mobility can point to torn muscles, overstretching, or joint issues.
Tingling, numbness, or burning sensations: Discomfort that persists during rest or movement might be signs of nerve involvement or pinched nerves.
Nerve impingement: Persistent sciatic or femoral nerve compression leads to ongoing pain, weakness, or sensory changes requiring medical evaluation.
Varicose veins and circulatory problems: Leg pain associated with visible varicose veins, heaviness, or skin discoloration suggests circulatory insufficiency or blood clots.
Prolonged or worsening pain: Ongoing discomfort that lasts several days or intensifies over time necessitates professional assessment.
Changes in skin temperature or color: Pallor, coolness, or bluish tint of the skin indicate circulation issues demanding urgent care.
Strategies to Prevent Leg Muscle Pain
While some injuries are unavoidable, adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of leg muscle discomfort. Here are effective preventive measures:
Incorporate regular movement and avoid prolonged periods of inactivity, especially during long journeys. Standing or walking periodically helps maintain healthy blood flow and reduces the risk of blood clots.
Maintain a balanced, healthy weight to reduce undue pressure on your joints and muscles. Excess weight increases strain, especially on the knees and hips.
Wear suitable footwear that provides adequate support. If you are prone to falls or have mobility issues, use assistive devices and conduct safety audits at home to minimize hazards.
Limit alcohol intake, as excessive consumption can impair judgment, lead to dehydration, and increase risk of falls or injuries. Women are advised to limit to one drink per day, while men should not exceed two drinks.
Monitor and control blood pressure and cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary. Good vascular health helps prevent circulatory-related leg issues.
Increase intake of potassium-rich foods such as bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, and lean meats to support healthy muscle function and prevent cramps.
Engage in regular physical activity that includes stretching and strengthening exercises. Proper warm-up and cooldown routines are crucial to avoid muscle strains and injuries.
If you experience persistent or worsening muscle pain, it is vital to seek medical attention promptly. Simple remedies like applying ice packs, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, and performing gentle stretching exercises can provide temporary relief for minor issues like cramps or fatigue. However, persistent symptoms require professional diagnosis to address underlying causes effectively.