Complete Guide to Epilepsy: Causes, Diagnosis, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide covers epilepsy's causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment options, including medication and emerging therapies. It emphasizes the importance of proper diagnosis, medication adherence, and lifestyle adjustments to effectively manage seizures and improve patients' quality of life.
Complete Guide to Epilepsy: Causes, Diagnosis, and Effective Treatment Strategies
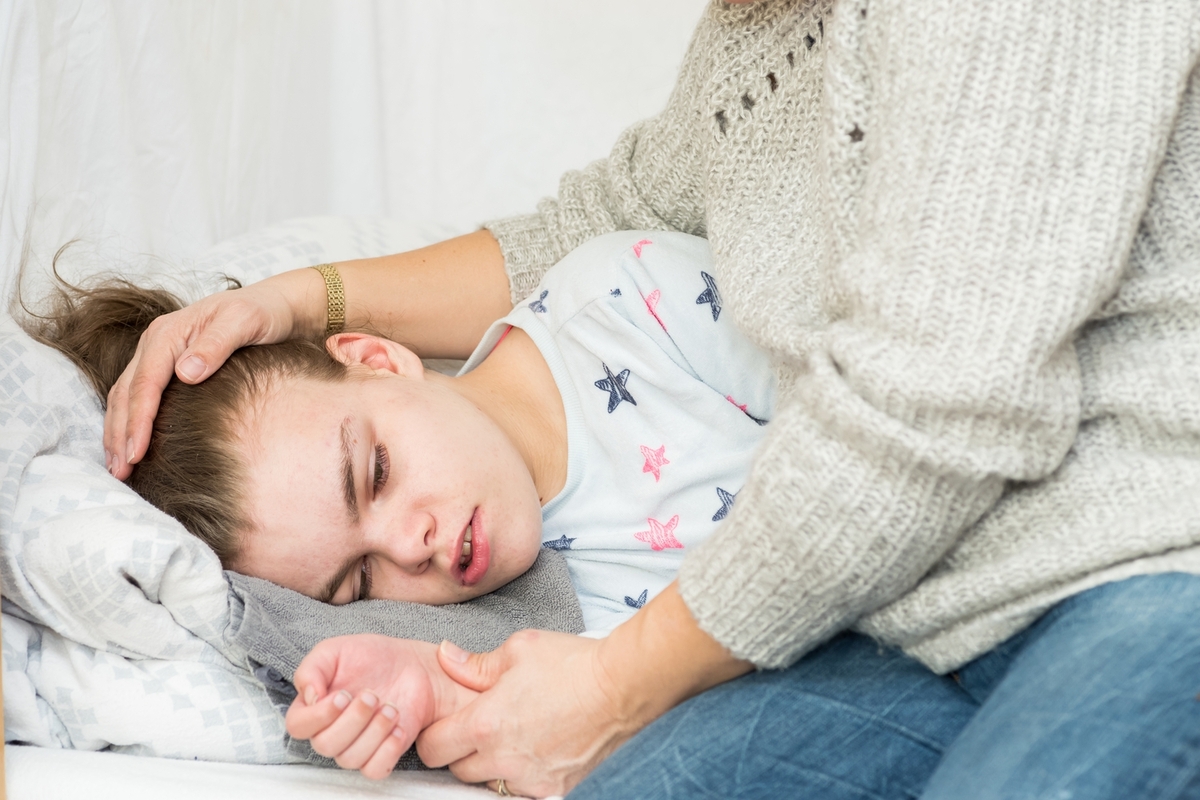
Epilepsy is a complex neurological disorder that affects millions worldwide, characterized primarily by recurrent seizures that arise due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These seizures can manifest in various ways, impacting an individual's mental, sensory, or motor functions temporarily. Because of its diverse symptoms and underlying causes, epilepsy presents unique challenges in management and treatment. Understanding the nature of epilepsy, identifying its triggers, and exploring the latest treatment options are crucial steps toward improving quality of life for those affected.
Epilepsy can develop at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in young children and older adults. Its symptoms vary widely, depending on the area of the brain involved and the type of seizure. Some individuals experience subtle signs such as brief lapses in awareness, while others endure intense convulsions. Recognizing the signs and seeking early diagnosis are vital for effective management.
Triggers for epileptic seizures are varied and can include head injuries, chemical imbalances within the brain, stroke, substance abuse like alcohol, or complications during birth. In some cases, no clear cause is identified, which complicates treatment efforts. It is also important to differentiate epilepsy from febrile seizures, which are typically caused by a high fever in children and generally do not signify a chronic neurological condition.
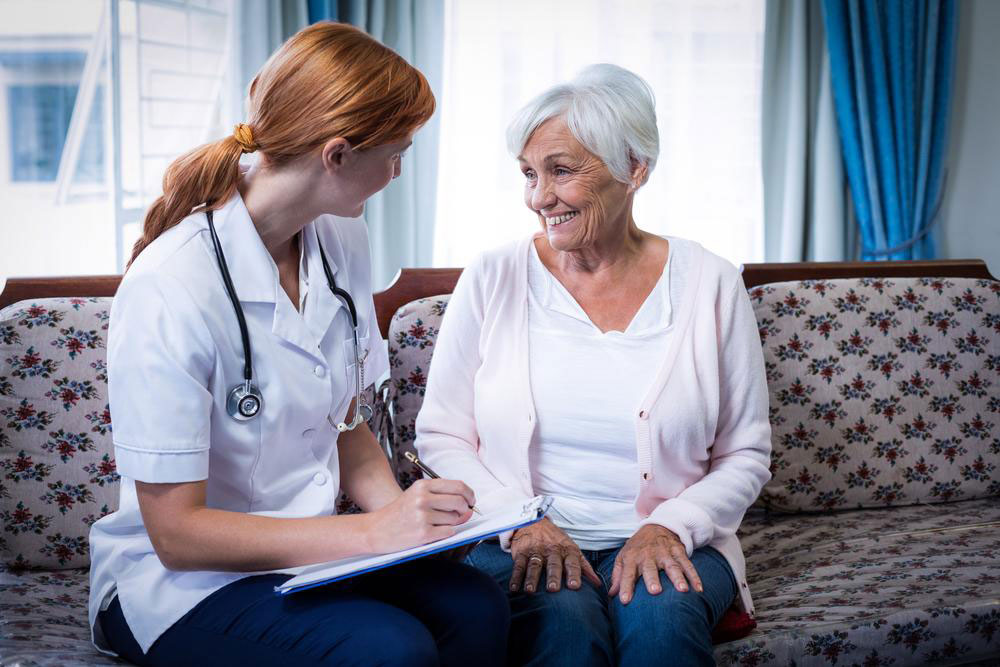
Diagnosing epilepsy involves a combination of medical history review, physical and neurological examinations, and specialized tests. Electroencephalograms (EEGs) are commonly used to detect abnormal brain activity, while neuroimaging techniques like MRI or CT scans help identify structural abnormalities. Accurate diagnosis is essential because treatment strategies vary based on seizure type, frequency, and underlying causes.
Management of epilepsy is multifaceted, with medication being the cornerstone of treatment for many patients. While a complete cure remains elusive for some, effective control of seizures is achievable through tailored pharmacological therapy combined with lifestyle adjustments.
One of the most frequently prescribed medications for epilepsy is Topiramate, branded as Topamax. This drug has been widely recognized for its efficacy in reducing seizure frequency in both pediatric and adult patients. When administered correctly, Topiramate generally exhibits a favorable side effect profile, making it a preferred choice for many neurologists.
Adherence to prescribed dosages is paramount. Deviating from the recommended intake can lead to adverse effects or reduced effectiveness. Common side effects associated with Topiramate include nausea, dizziness, fatigue, diarrhea, depression, unintended weight loss, and tingling sensations. More rarely, some individuals may experience nasal or throat discomfort. Pregnant women are advised to avoid using Topiramate due to potential risks to the developing fetus.
To minimize drowsiness or fatigue, taking the medication at night can be beneficial. If a dose is missed, patients should consult their healthcare provider for guidance rather than doubling the dose. Initiating treatment requires thorough medical evaluation and history-taking to ensure suitability and safety.
It is crucial to understand that Topiramate and other anti-epileptic drugs are prescription medications. They should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Self-medicating or attempting to treat seizures without proper medical consultation can be dangerous, potentially leading to severe health risks or fatal outcomes. In the event of sudden, uncontrolled seizures, immediate hospital care is necessary for stabilization and further assessment.
While medication greatly enhances seizure control, it’s important to note that epilepsy may not always be entirely curable. Regular follow-up appointments, medication adjustments, and continuous monitoring are essential components of effective disease management. Moreover, lifestyle modifications, such as adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding known triggers, can significantly reduce seizure frequency.
In recent years, advances in neurology and neurotechnology are opening new avenues for epilepsy treatment, including surgical interventions, vagus nerve stimulation, and responsive neurostimulation devices. These options are typically considered in cases where medication fails to provide adequate control.
Overall, living with epilepsy requires a comprehensive understanding of the disorder and a collaborative approach involving healthcare providers, family, and patients. Empowering individuals with knowledge about their condition and treatment options can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.