Effective Strategies for Treating Toenail Fungal Infections and Promoting Nail Health
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for treating toenail fungal infections, highlighting medication options, surgical methods, prevention tips, and the importance of early intervention. Learn how to combat onychomycosis effectively and restore healthy nails with proven treatments and care practices.

Comprehensive Approaches to Combat Toenail Fungal Infections and Restore Nail Health
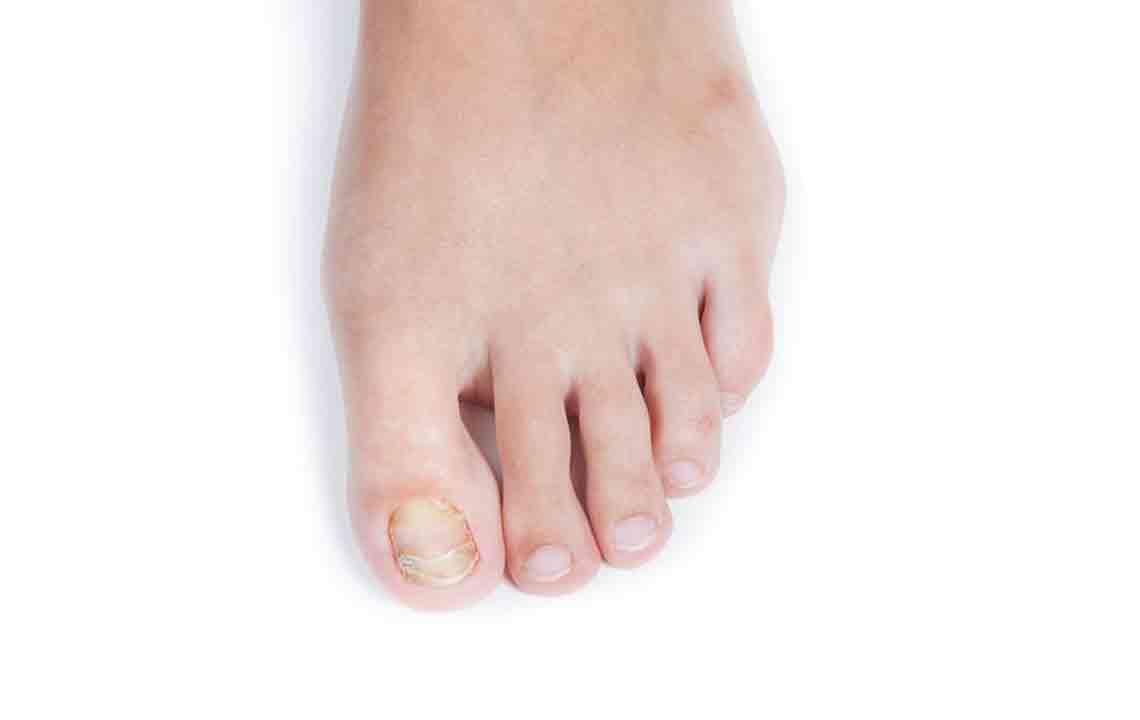
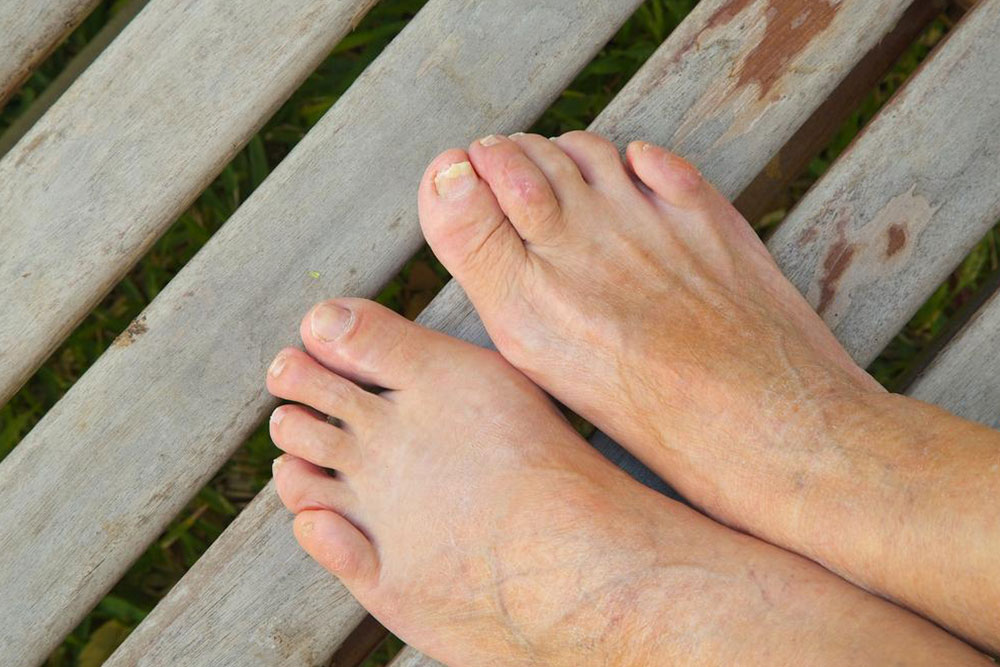
Toenail fungal infections, medically known as onychomycosis, are a common nail disorder that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. Characterized by yellow or white patches under the nail, this condition can cause nails to become thickened, brittle, discolored, and sometimes deformed if left untreated. The infection can also spread to surrounding skin, leading to discomfort, bad odor, and potential secondary bacterial infections. Understanding effective treatment options and early intervention are crucial to prevent worsening of the condition and maintain overall foot health.
Fortunately, advances in dermatology and pharmacology offer a variety of effective treatments tailored to different severity levels and individual needs. In this detailed guide, we explore the most reliable and proven strategies to eliminate toenail fungus efficiently, restore the appearance of your nails, and prevent recurrrence. Whether mild or severe, there's a treatment approach suitable for everyone.
Understanding Toenail Fungal Infection
Before diving into treatment options, it’s essential to understand what causes toenail fungal infections. The fungi responsible, mainly dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds, thrive in warm, moist environments. Factors such as sweating excessively, wearing tight shoes, walking barefoot in public showers, pools, or gyms, and having compromised immune systems can increase the risk of infection. Once the fungi invade the nail bed through small cuts or weakened skin barriers, they begin to proliferate, leading to the hallmark symptoms of discoloration, thickening, and nail破碎 or separation from the nail bed.
Early-stage infections might be subtle, with only slight discoloration or thickening, but without prompt treatment, the infection can worsen, leading to more pronounced deformity and discomfort. Chronic infections not only impair nail appearance but also pose a risk of spreading to other nails and skin. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are vital.
Key Treatment Strategies for Toenail Fungus
Effectively treating toenail fungus involves a combination of pharmacological, topical, and sometimes surgical interventions, tailored to the severity, type of fungus, and patient health status. The goal is to eradicate the infection, restore nail health, and prevent recurrence.
Below are the primary treatment modalities that have proven effective in managing toenail fungal infections:
Systemic Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal drugs are often considered the most effective method, especially in moderate to severe cases. These medications function by penetrating the nail tissue and eliminating the fungi from within. Commonly prescribed drugs include terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole. The typical treatment duration ranges from 6 to 12 weeks, though it may extend depending on the response and severity of infection. The new nail usually grows in healthy once the infected portion has been replaced.
Despite their effectiveness, these drugs require careful monitoring because of potential side effects such as liver toxicity, skin rash, or gastrointestinal discomfort. Regular blood tests and medical supervision are necessary to ensure patient safety. Patients are advised to inform their healthcare providers about any pre-existing conditions or medications that might interact with these antifungal agents.
Topical Antifungal Treatments
Topical medications are a cornerstone in treating mild to moderate cases and serve as an adjunct in more severe infections. These include medicated nail lacquers (such as ciclopirox or amorolfine) and antifungal creams or solutions that are applied directly onto the affected nails and surrounding skin.
Topical treatments are generally used over extended periods—often several months to a year—to ensure complete eradication of the fungus. Consistent daily application is crucial for effectiveness. These medications work by disrupting the cell wall of the fungi, preventing further growth and spreading. In some cases, surgical removal of the infected part of the nail enhances drug penetration and accelerates recovery.
Surgical and Laser Interventions
When medications alone fail to clear the infection, or in cases of severe nail dystrophy, surgical options may be considered. The surgical approach involves the removal of the infected nail to allow direct access to the nail bed for antifungal applications and to reduce fungal load.
In addition, laser therapy has emerged as a non-invasive alternative, where directed laser beams heat and destroy fungal cells. While some clinics report promising results, the effectiveness varies, and multiple sessions are often necessary. Laser treatments are generally safe and do not involve anesthesia but can be costly.
In persistent and refractory cases, permanent removal of the nail may be recommended to prevent recurrent infections and restore normal foot health.
Preventive Measures and Home Care
Preventing toenail fungal infections is equally important as treatment. Good foot hygiene practices include keeping feet dry and clean, avoiding walking barefoot in communal areas, wearing breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks, and disinfecting footwear regularly. Additionally, trimming nails straight across, avoiding nail trauma, and not sharing personal grooming items can significantly reduce risk.
For ongoing prevention, consider using antifungal powders or sprays, especially if you have a history of fungal infections. Maintaining overall immune health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest can also bolster resistance against fungal pathogens.
Consultation and Professional Diagnosis
If you notice signs of toenail fungus—discoloration, thickening, crumbling, or separation from the nail bed—it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. A healthcare professional can perform proper diagnostics, including microscopy or fungal cultures, to confirm the infection and determine its severity. Early diagnosis facilitates effective treatment, reducing the risk of complications and long-term deformity.
Addressing toenail fungal infections early not only restores the aesthetic appearance of your nails but also prevents secondary infections and potential spreading to other nails or skin areas. Remember, persistent or worsening symptoms should always prompt professional assessment.
In conclusion, managing toenail fungus requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, home care, and preventive strategies. With proper intervention, you can restore healthy nails, improve your foot health, and regain confidence in your appearance.