Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by skin rashes, muscle weakness, and systemic symptoms. Recognizing early signs like characteristic rashes, muscle discomfort, and systemic indicators is essential for prompt diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide details key symptoms such as skin rashes, muscle weakness, calcium deposits, swallowing issues, and more, helping patients and caregivers seek timely medical help and improve quality of life through appropriate treatments.

An In-Depth Look into Early Signs and Common Symptoms of Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a rare and complex autoimmune disease that affects both the skin and muscles. It can lead to inflammation, swelling, and weakness in various parts of the body. Although it can occur at any age, it most commonly affects children between the ages of 5 and 15, as well as adults in their 40s to 60s. The exact cause remains unclear, and currently, there is no definitive cure for dermatomyositis. Instead, treatment focuses on managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing relapses or further complications. Early diagnosis and timely intervention are essential for improving patient outcomes. Understanding the key signs and symptoms can help patients and caregivers seek medical attention promptly, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of treatment plans.
1. Distinctive Skin Rash
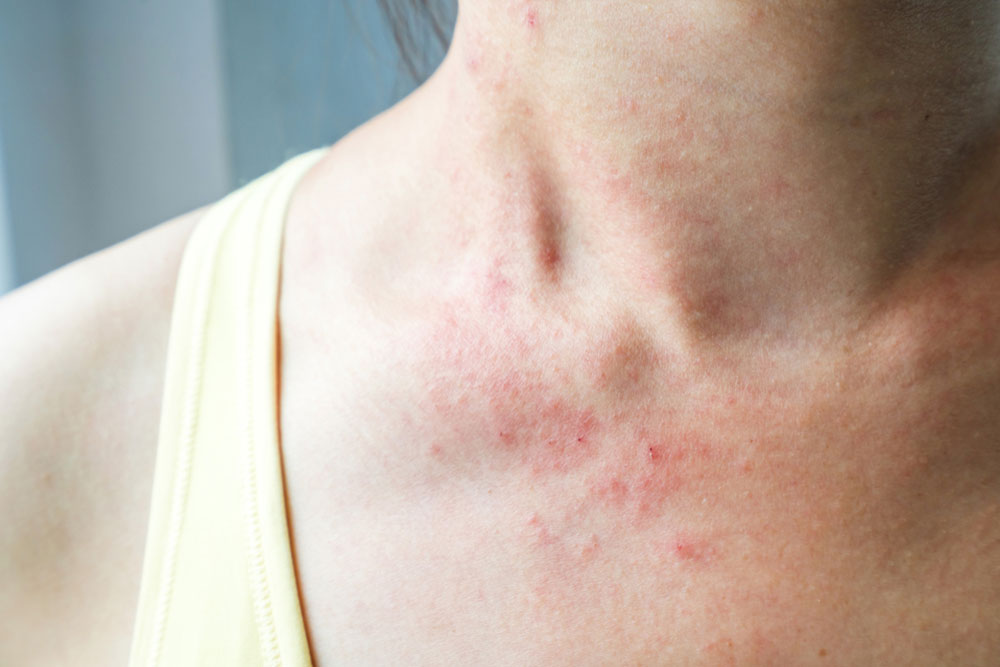
One of the most noticeable and characteristic signs of dermatomyositis is a skin rash that often appears as a violet or dusky red discoloration. This rash may be swollen, itchy, and sensitive, and it most frequently appears on sun-exposed parts of the body. Common locations include the face, especially around the eyelids, as well as the knuckles, elbows, knees, chest, neck, and back. The rash can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions; hence, awareness of its distinctive appearance is crucial for early detection. In some cases, the rash may be accompanied by a photosensitive reaction, worsening with sun exposure. Recognizing this rash early can lead to faster diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly mitigate disease progression and reduce discomfort.
2. Persistent Muscle Weakness and Pain
Muscle discomfort in dermatomyositis is often progressive and not linked to injury or strenuous activity. Patients commonly experience persistent muscle weakness, making routine activities like climbing stairs, rising from a chair, or lifting objects difficult. The weakness may initially be subtle but tends to worsen over time if untreated. Some patients also report muscle tenderness, stiffness, or aching, which can significantly impair daily functioning. Recognizing muscle symptoms early and differentiating them from other causes of muscle pain is vital for diagnosis. Muscle biopsies, blood tests for muscle enzymes, and electromyography are typically used to confirm the condition. Early therapeutic intervention can help preserve muscle strength and prevent irreversible damage.
3. Calcium Deposits in the Skin and Muscles
In children with dermatomyositis, the formation of calcium deposits within the skin, muscles, or connective tissues is a common complication. These deposits can appear as hardened nodules or lumps that are sometimes tender or inflamed. The deposits may interfere with movement, cause disfigurement, or lead to secondary infections. Recognizing these calcium accumulations early is essential for managing the disease effectively. Treatments may include medications aimed at reducing calcium deposits, physical therapy, or other interventions to maintain mobility and minimize discomfort. Early detection of calcifications can also prevent further tissue damage and improve the patient's quality of life.
4. Systemic Symptoms: Fever and Weight Loss
Systemic signs such as fever, unexplained weight loss, and malaise are common in active phases of dermatomyositis. These symptoms reflect widespread inflammation in the body and can be mistaken for infections or other autoimmune disorders. When these systemic manifestations accompany skin rash or muscle weakness, they strongly suggest a broader inflammatory process at work. Laboratory tests, including blood counts, inflammatory markers (like ESR or CRP), and imaging studies, are used for evaluation. Prompt medical assessment is crucial, as these symptoms can signal an active disease phase requiring aggressive management to prevent irreversible organ damage.
5. Swallowing Difficulties (Dysphagia)
Myositis can involve the muscles of the oropharynx and esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. Patients may feel like food is stuck in their throat, experience choking or coughing during meals, and report a sensation of weakness in the neck or throat muscles. This complication can be serious, increasing the risk of aspiration pneumonia and malnutrition. Early recognition and management, including speech therapy, dietary modifications, and immunosuppressive treatments, are crucial to prevent further complications. In some cases, difficulty swallowing may be the first sign prompting further investigation into underlying myositis.
6. Breathing Challenges
Progressive diaphragm or chest muscle involvement can cause breathing difficulties, especially shortness of breath or respiratory fatigue. This symptom warrants immediate evaluation as it indicates potential respiratory muscle weakness. Patients might notice increased effort when breathing, particularly during exertion or at rest in severe cases. Imaging studies like chest X-rays, pulmonary function tests, and muscle assessments can help determine the extent of muscle inflammation. Managing respiratory symptoms often involves corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and physical therapy to strengthen respiratory muscles and improve lung function.
7. Voice Changes and Hoarseness
Vocal changes, including hoarseness, strain, or loss of voice, can be linked to inflammation of the laryngeal muscles involved in speech and voice production. These symptoms may be subtle at first but can deteriorate if the underlying muscle inflammation worsens. Persistent hoarseness alongside other symptoms like swallowing difficulty or breathing issues calls for urgent medical evaluation. Speech therapy, corticosteroid therapy, and other immunosuppressive treatments can help reduce inflammation and restore normal voice function.
8. Widespread Joint Pain and Stiffness
Many individuals with dermatomyositis experience joint complaints, including aches, swelling, and stiffness. Although joint pain can occur in various conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, persistent joint discomfort in combination with muscle weakness and skin rash should prompt consideration of dermatomyositis. These joint symptoms can limit mobility and may require anti-inflammatory medications or physical therapy to maintain function. Recognizing overlap symptoms helps ensure proper diagnosis and effective management.
9. Skin Bumps and Nodules
Patients may develop skin bumps, particularly over areas like the elbows, knees, or other bony prominences. These bumps can be soft or hard, inflamed or asymptomatic, and may sometimes result from trauma or injury. However, in the context of dermatomyositis, such bumps may represent granulomatous skin changes or calcinosis. Accurate assessment and biopsy can distinguish skin-related manifestations of dermatomyositis from other dermatological conditions. Early intervention can prevent progression and complications related to skin lesions.
10. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
In children and sometimes adults, dermatomyositis can involve the gastrointestinal tract, leading to ulcers, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and heartburn. These symptoms are due to inflammation and damage to the GI mucosa. Recognizing gastrointestinal involvement early allows for targeted treatment, which may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and supportive care. Persistent stomach pain or changes in bowel habits should prompt medical review to prevent complications like bleeding or perforation.
11. Pale and Discolored Skin (Raynaud’s Phenomenon)
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a condition associated with dermatomyositis where fingers, toes, earlobes, and facial skin turn pale or bluish and feel cold or numb upon exposure to cold temperatures. Patients may experience tingling, prickling sensations, or loss of sensation in affected areas. Recognizing these vascular changes early can help manage vascular symptoms and prevent tissue damage. The phenomenon indicates underlying vascular involvement and warrants comprehensive evaluation and management involving vascular regimens, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes medications to improve blood flow.